Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

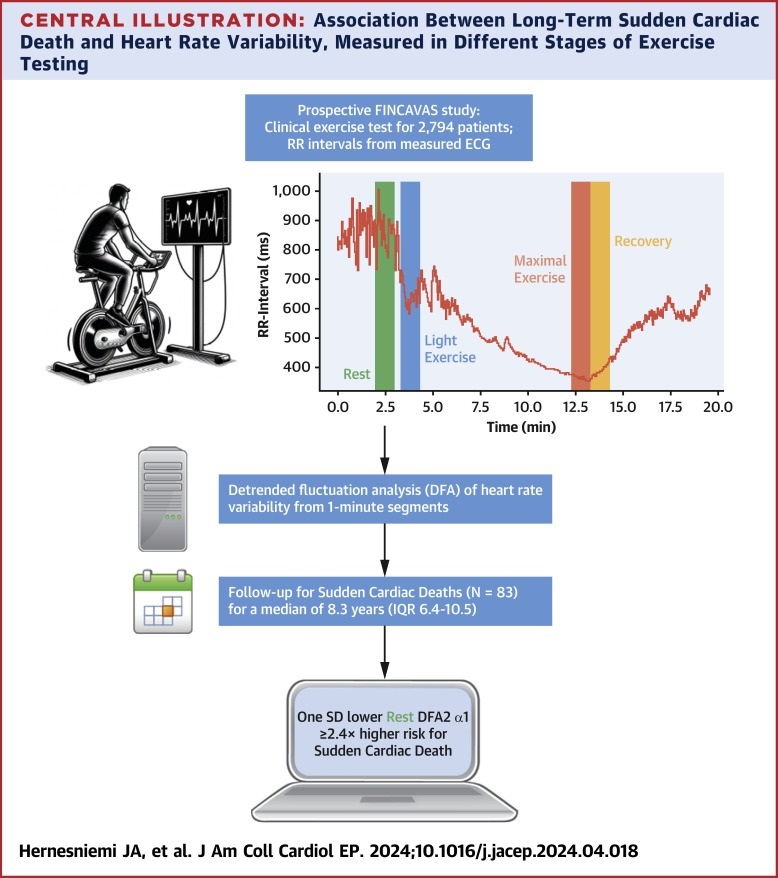
- Breakthrough Computational Method Predicts Sudden Cardiac Death
- GPS-Like Smart Pills with AI Provide Real-Time 3D Monitoring Of Gastrointestinal Health
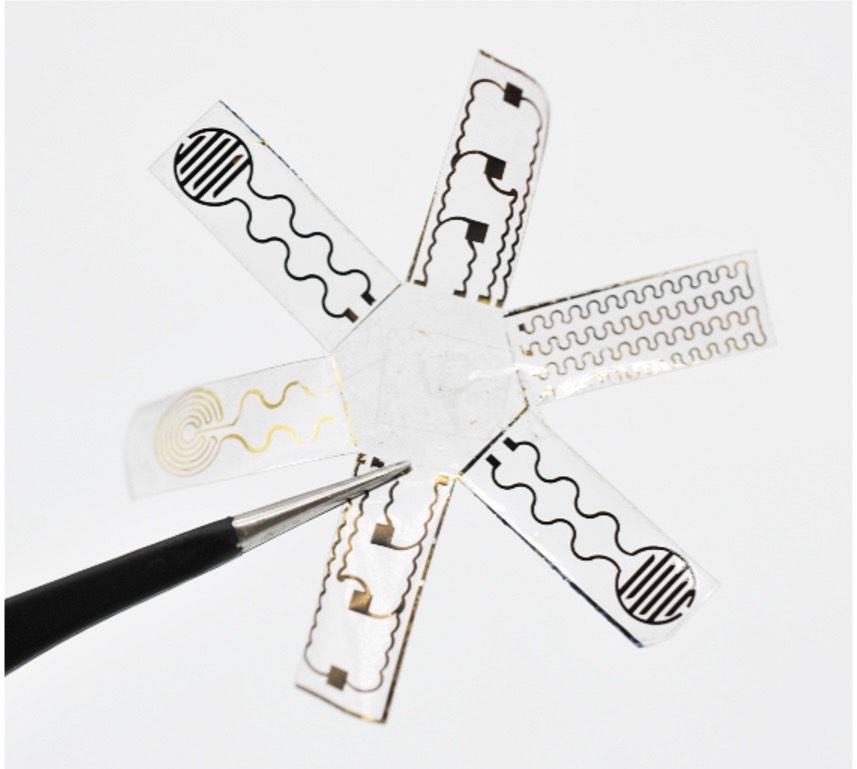
- Soft Robots with Electronic Skins and Artificial Muscles to Provide Medical Treatment
- Bioengineering Breakthrough to Improve Bone Regeneration Treatments
- AI Camera Technology Helps Doctors Quickly Assess Severity of Infections
- Wirelessly Activated Robotic Device Aids Digestion in Patients with Compromised Organs
- Glowing Dye Helps Surgeons to Remove Hidden Prostate Cancer Cells in Real-Time
- Early Minimally Invasive Surgery Improves Intracerebral Hemorrhage Stroke Outcomes
- Early EVD Insertion Improves Surgical Outcome in Traumatic Brain Injury
- New Machine Learning Method Better Predicts Spine Surgery Outcomes
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- MEDICA INNOVATION FORUM for the Healthcare Innovations of the Future
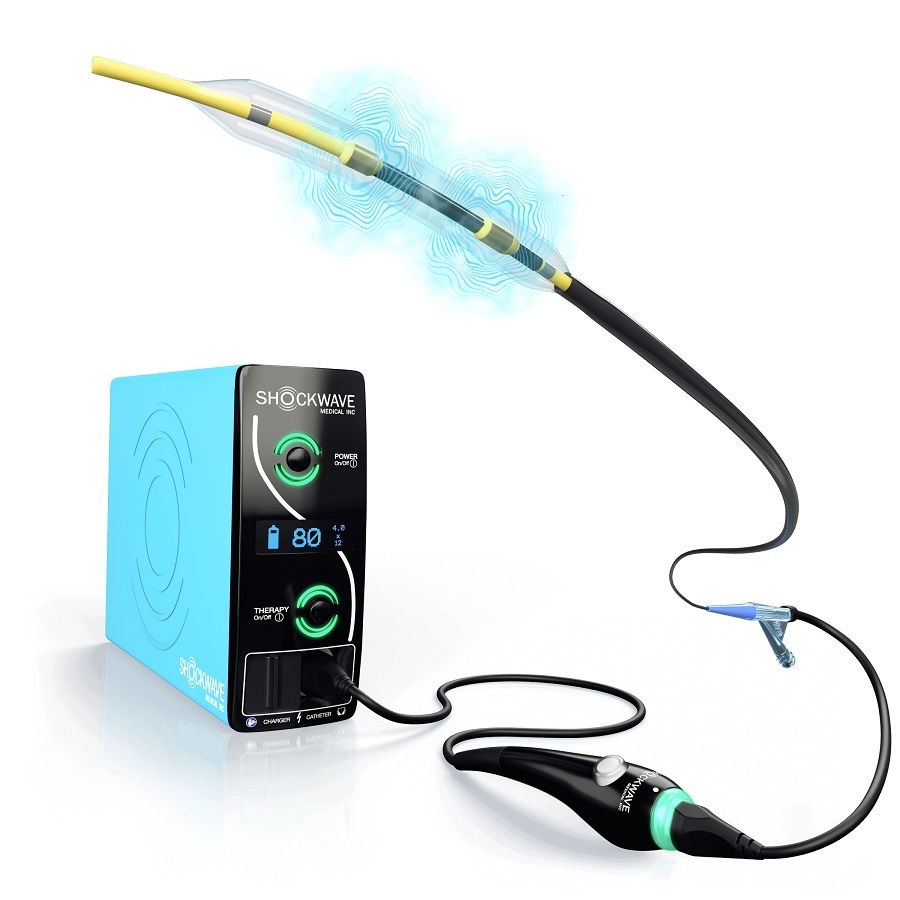
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Medical Device Company Shockwave Medical
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
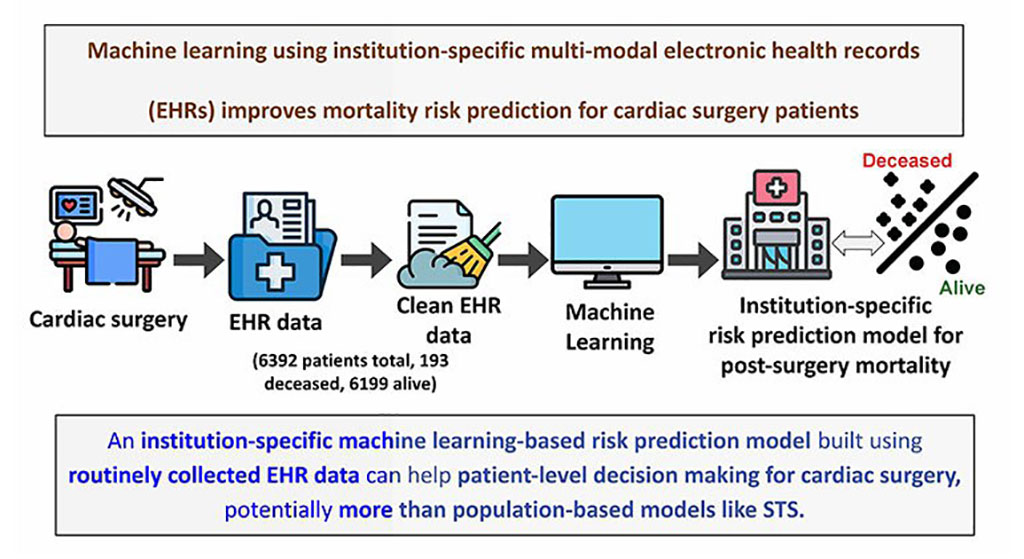
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
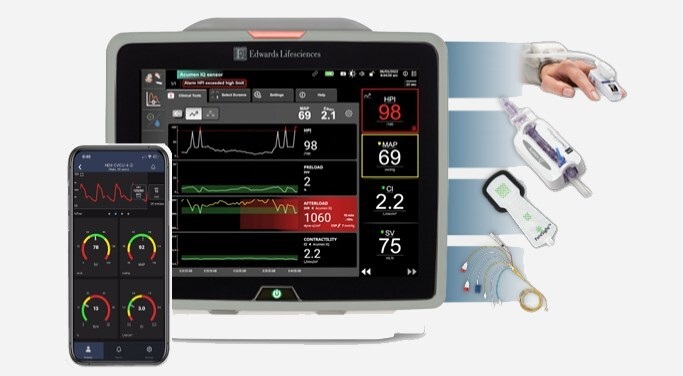
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Breakthrough Computational Method Predicts Sudden Cardiac Death
- GPS-Like Smart Pills with AI Provide Real-Time 3D Monitoring Of Gastrointestinal Health
- Soft Robots with Electronic Skins and Artificial Muscles to Provide Medical Treatment
- Bioengineering Breakthrough to Improve Bone Regeneration Treatments
- AI Camera Technology Helps Doctors Quickly Assess Severity of Infections
- Wirelessly Activated Robotic Device Aids Digestion in Patients with Compromised Organs
- Glowing Dye Helps Surgeons to Remove Hidden Prostate Cancer Cells in Real-Time
- Early Minimally Invasive Surgery Improves Intracerebral Hemorrhage Stroke Outcomes
- Early EVD Insertion Improves Surgical Outcome in Traumatic Brain Injury
- New Machine Learning Method Better Predicts Spine Surgery Outcomes
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- MEDICA INNOVATION FORUM for the Healthcare Innovations of the Future
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Medical Device Company Shockwave Medical
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use


















.jpg)