Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

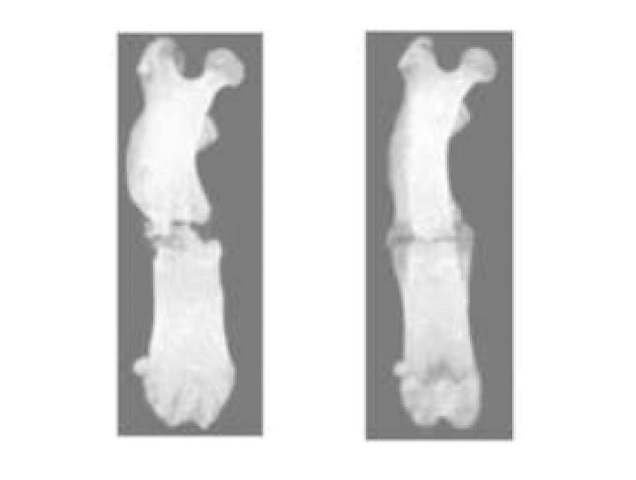
- Plasma Irradiation Promotes Faster Bone Healing
- New Device Treats Acute Kidney Injury from Sepsis
- Study Confirms Safety of DCB-Only Strategy for Treating De Novo Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
- Revascularization Improves Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- AI-Driven Prediction Models Accurately Predict Critical Care Patient Deterioration
- Computational Models Predict Heart Valve Leakage in Children
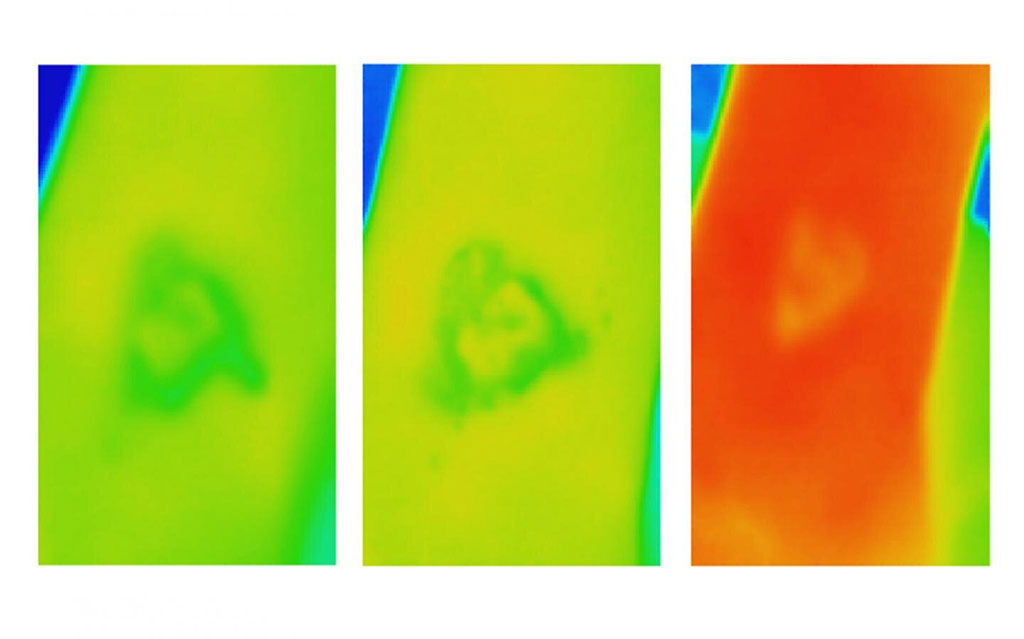
- World’s First Microscopic Probe to Revolutionize Early Cancer Diagnosis
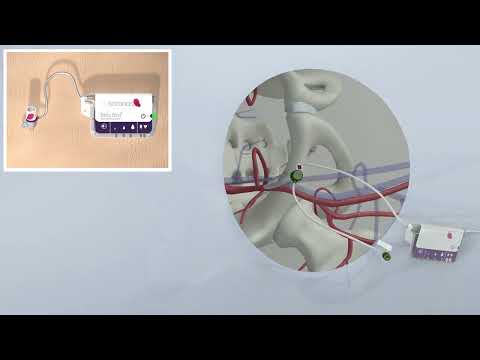
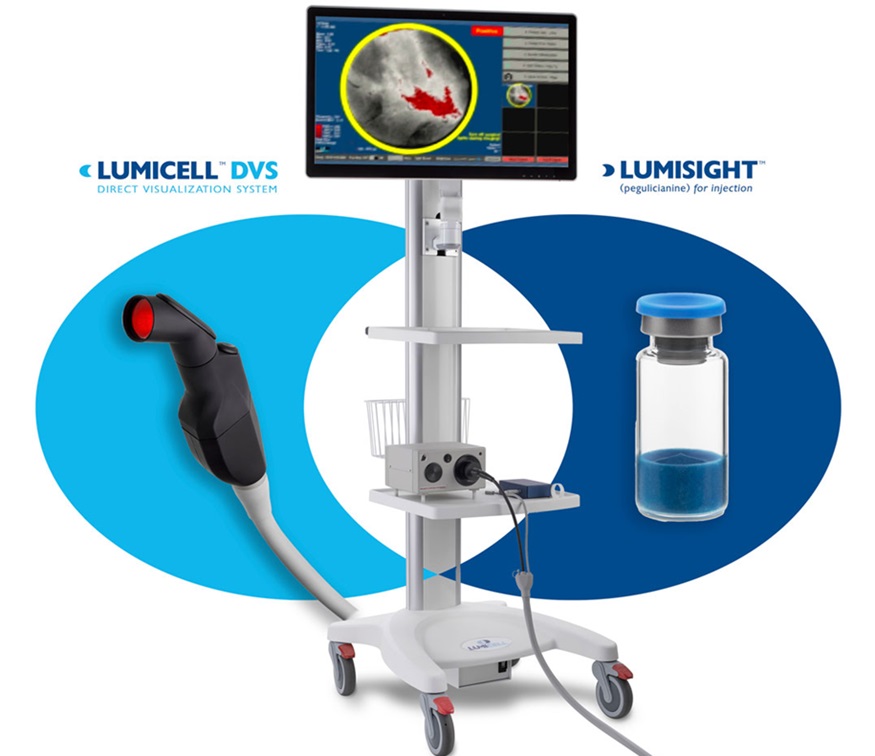
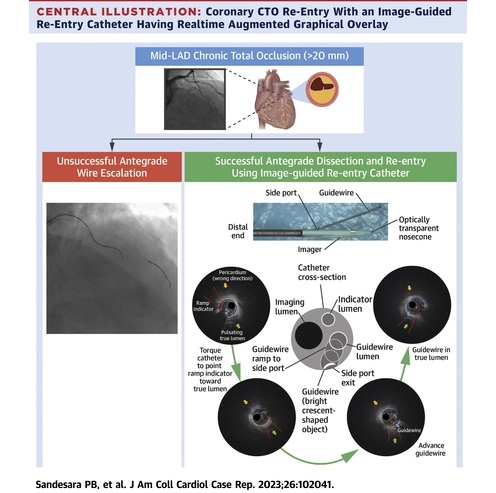
- Breakthrough Device Enables Clear and Real-Time Visual Guidance for Effective Cardiovascular Interventions
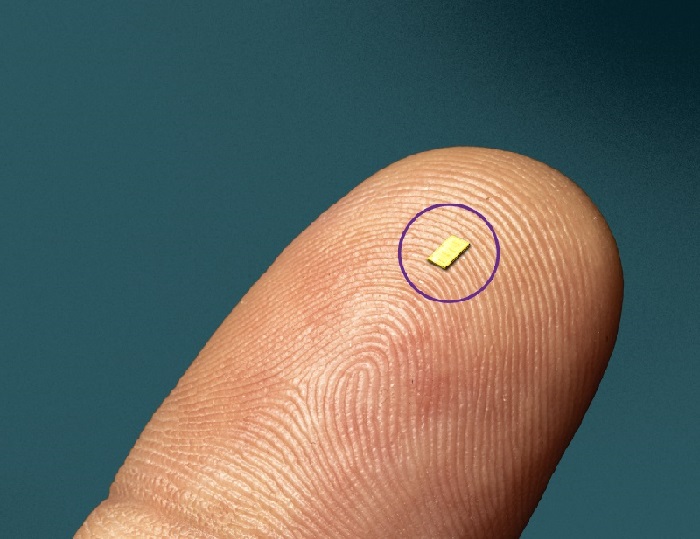
- World’s Smallest Implantable Brain Stimulator Demonstrated in Human Patient
- Robotically Assisted Lung Transplants Could Soon Become a Reality
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Smart Hospital Beds Improve Accuracy of Medical Diagnosis
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Medical Illumination Acquires Surgical Lighting Specialist Isolux
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
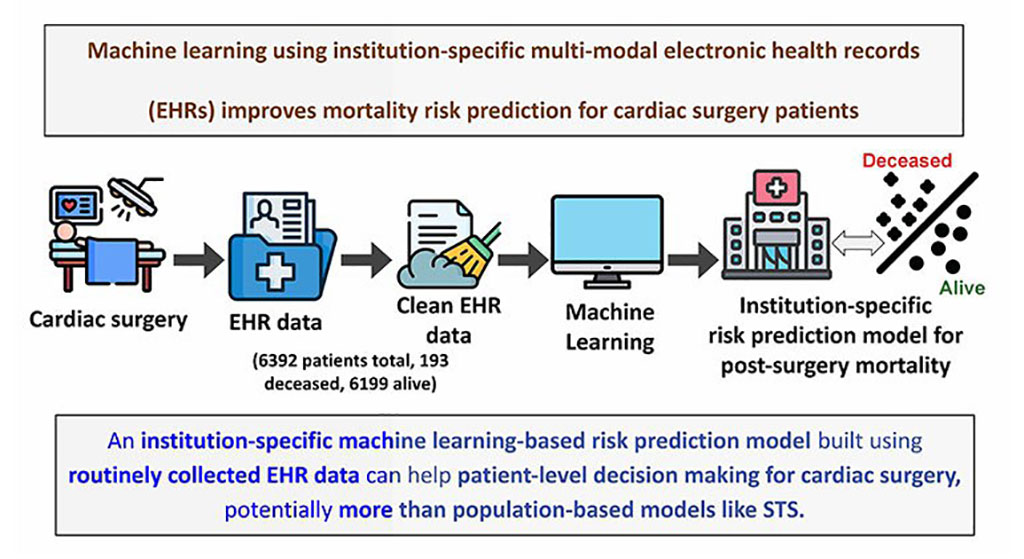
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- AI Diagnostic Tool Accurately Detects Valvular Disorders Often Missed by Doctors
- New Model Predicts 10 Year Breast Cancer Risk
- AI Tool Accurately Predicts Cancer Three Years Prior to Diagnosis
- Ground-Breaking Tool Predicts 10-Year Risk of Esophageal Cancer
- AI Tool Analyzes Capsule Endoscopy Videos for Accurately Predicting Patient Outcomes for Crohn’s Disease
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use
- Unique Quantitative Diagnostic System Enables Immediate Diagnosis and Treatment at POC
- POC Myocardial Infarction Test Delivers Results in 17 Minutes

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Plasma Irradiation Promotes Faster Bone Healing
- New Device Treats Acute Kidney Injury from Sepsis
- Study Confirms Safety of DCB-Only Strategy for Treating De Novo Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
- Revascularization Improves Quality of Life for Patients with Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- AI-Driven Prediction Models Accurately Predict Critical Care Patient Deterioration
- Computational Models Predict Heart Valve Leakage in Children
- World’s First Microscopic Probe to Revolutionize Early Cancer Diagnosis
- Breakthrough Device Enables Clear and Real-Time Visual Guidance for Effective Cardiovascular Interventions
- World’s Smallest Implantable Brain Stimulator Demonstrated in Human Patient
- Robotically Assisted Lung Transplants Could Soon Become a Reality
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Smart Hospital Beds Improve Accuracy of Medical Diagnosis
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Medical Illumination Acquires Surgical Lighting Specialist Isolux
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- AI Diagnostic Tool Accurately Detects Valvular Disorders Often Missed by Doctors
- New Model Predicts 10 Year Breast Cancer Risk
- AI Tool Accurately Predicts Cancer Three Years Prior to Diagnosis
- Ground-Breaking Tool Predicts 10-Year Risk of Esophageal Cancer
- AI Tool Analyzes Capsule Endoscopy Videos for Accurately Predicting Patient Outcomes for Crohn’s Disease
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use
- Unique Quantitative Diagnostic System Enables Immediate Diagnosis and Treatment at POC
- POC Myocardial Infarction Test Delivers Results in 17 Minutes