Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Sophisticated Machine-Learning Approach Uses Patient EHRs to Predict Pneumonia Outcomes
- Early TAVR Benefits Patients with Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
- First-Of-Its-Kind Experimental Therapy Enhances Tissue Repair After Heart Attack
- AI Model Predicts Patients at Most Risk of Complication During Treatment for Advanced Kidney Failure
- AI Model Predicts Patients’ Risk of Developing and Worsening Disease from ECGs
- Miniature Soft Lithium-Ion Battery Could Be Used as Defibrillator During Surgery
- TAVI Procedure Supported by Radial Artery Access Reduces Bleeding Complications
- Portable Surgical Robot Seamlessly Integrates into Any OR for Performing Cholecystectomy Procedures
- New Thoracic Surgery Risk Calculators Support Preoperative Decision-Making
- Surgical Platform with Miniature Humanoid-Shaped Robotic Arms Provides Human Level Dexterity
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
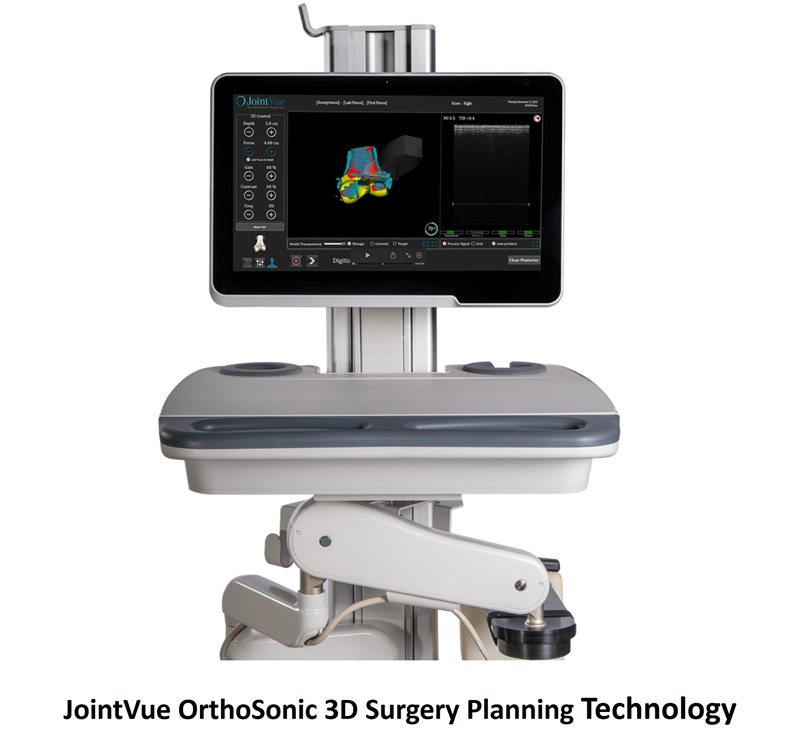
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
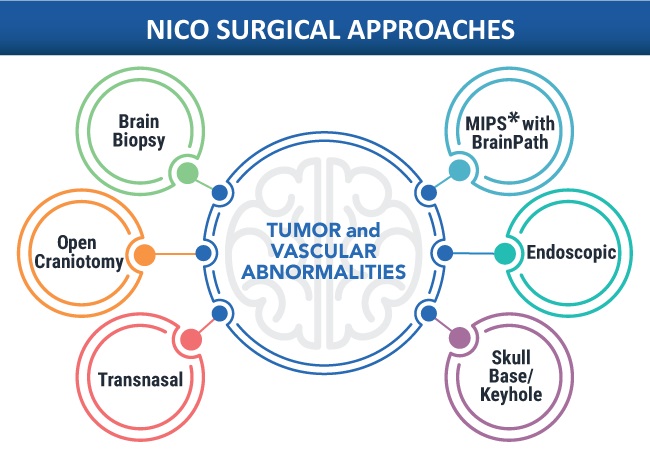
- Stryker Completes Acquisition of NICO Corporation
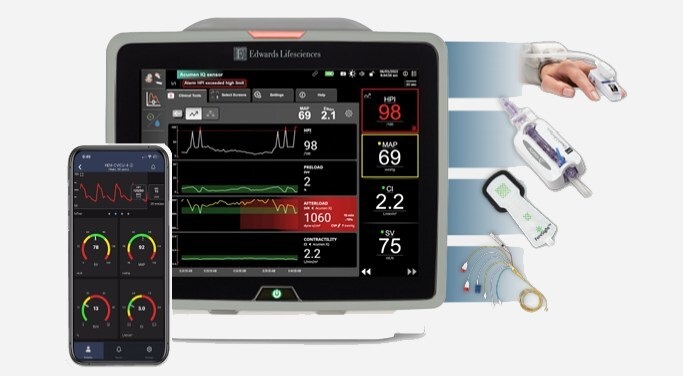
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
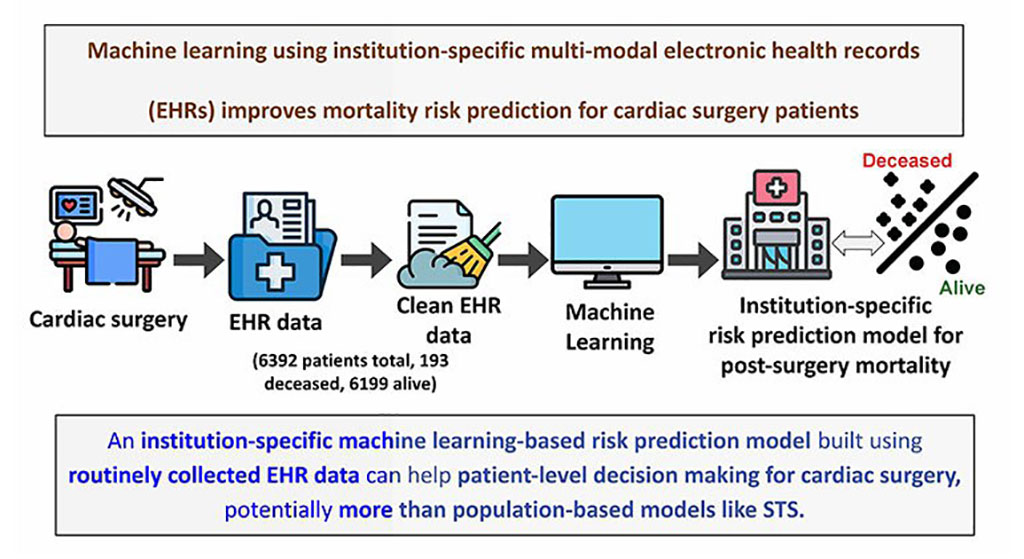
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Sophisticated Machine-Learning Approach Uses Patient EHRs to Predict Pneumonia Outcomes
- Early TAVR Benefits Patients with Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
- First-Of-Its-Kind Experimental Therapy Enhances Tissue Repair After Heart Attack
- AI Model Predicts Patients at Most Risk of Complication During Treatment for Advanced Kidney Failure
- AI Model Predicts Patients’ Risk of Developing and Worsening Disease from ECGs
- Miniature Soft Lithium-Ion Battery Could Be Used as Defibrillator During Surgery
- TAVI Procedure Supported by Radial Artery Access Reduces Bleeding Complications
- Portable Surgical Robot Seamlessly Integrates into Any OR for Performing Cholecystectomy Procedures
- New Thoracic Surgery Risk Calculators Support Preoperative Decision-Making
- Surgical Platform with Miniature Humanoid-Shaped Robotic Arms Provides Human Level Dexterity
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Smith+Nephew and JointVue Partner on Ultrasound Preoperative Planning in Robotics-Assisted Surgery
- Stryker Completes Acquisition of NICO Corporation
- BD Completes Acquisition of Critical Care from Edwards Lifesciences
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds


















.jpg)