Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient Care
Point of CareBusiness
Events

- Flexible Device Enables Sweat Gland Stimulation and Simultaneous Biosensing
- WHO Publishes First Global Guidelines to Reduce Bloodstream Infections from Catheter Use
- Innovative Material Paves Way for Next-Generation Wearable Devices
- Wireless Electronic Suture Enables Postoperative Long-Term Monitoring Of Soft Tissue
- Transcatheter Valve Replacement Outcomes Similar To Surgery, Finds Study
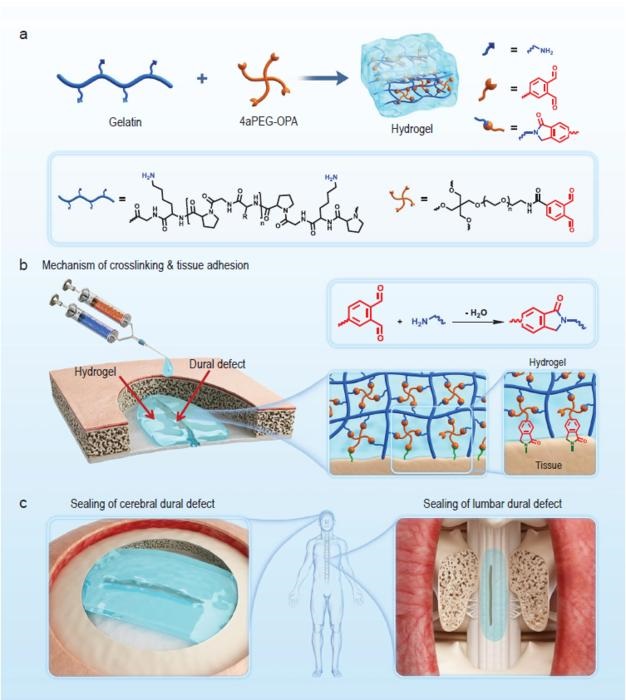
- New Hydrogel Sealant Effective at Sealing Dural Defects and Preventing Postoperative Adhesion
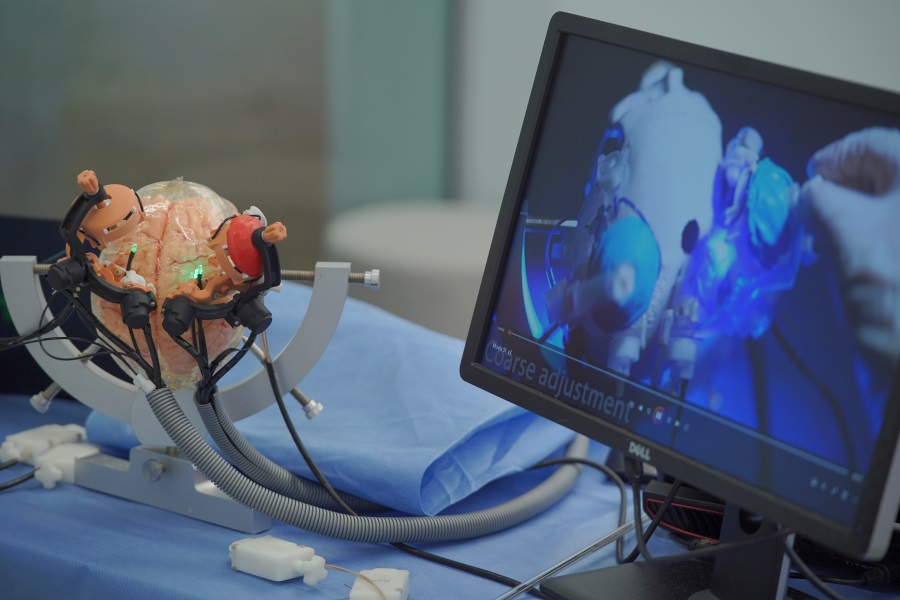
- MRI-Guided Multi-Stage Robotic Positioner Enhances Stereotactic Neurosurgery Precision
- AR Visualization System Improves Surgeons’ Capabilities and Spatial Awareness
- New Adhesive Hydrogel Coatings to Prolong Lifespan of Pacemakers and Medical Implants
- Maneuvering System Empowers Surgeons with Enhanced Control during Laparoscopic Procedures
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Medical Device Company Shockwave Medical
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
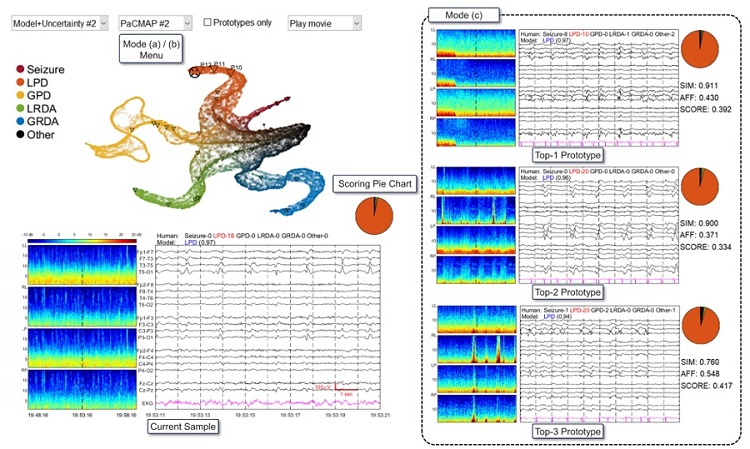
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient Care
Point of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient Care
Point of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Flexible Device Enables Sweat Gland Stimulation and Simultaneous Biosensing
- WHO Publishes First Global Guidelines to Reduce Bloodstream Infections from Catheter Use
- Innovative Material Paves Way for Next-Generation Wearable Devices
- Wireless Electronic Suture Enables Postoperative Long-Term Monitoring Of Soft Tissue
- Transcatheter Valve Replacement Outcomes Similar To Surgery, Finds Study
- New Hydrogel Sealant Effective at Sealing Dural Defects and Preventing Postoperative Adhesion
- MRI-Guided Multi-Stage Robotic Positioner Enhances Stereotactic Neurosurgery Precision
- AR Visualization System Improves Surgeons’ Capabilities and Spatial Awareness
- New Adhesive Hydrogel Coatings to Prolong Lifespan of Pacemakers and Medical Implants
- Maneuvering System Empowers Surgeons with Enhanced Control during Laparoscopic Procedures
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Medical Device Company Shockwave Medical
- Mindray to Acquire Chinese Medical Device Company APT Medical
- Olympus Acquires Korean GI Stent Maker Taewoong Medical
- Karl Storz Acquires British AI Specialist Innersight Labs
- Stryker to Acquire French Joint Replacement Company SERF SAS
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use