Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
Critical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Point-Of-Care EEG System Significantly Reduces Length of Patient Stay in ICU
- High-Quality Thin Film Conductor Paves Way for Wearable Electronics with Longer Life Batteries
- Intraoral Camera for Cancer Screening Eliminates Guesswork in Interpreting Clinical Findings
- AI Algorithm Non-Invasively Measures Intracranial Pressure in ICU Patients Following Traumatic Brain Injury
- Healthcare Device Powered By Body Heat Marks First Step Toward Battery-Free Wearable Electronics
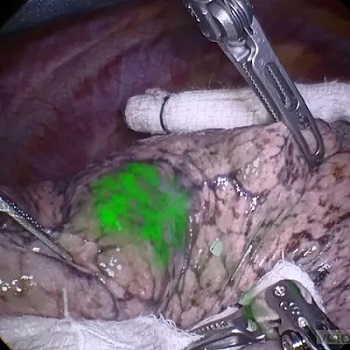
- Novel Fluorescent Imaging Agent Helps Surgeons Visualize Missed Lung Tumors
- EHR–Based Nudge Intervention for Surgeons to Reduce Breast Cancer Overtreatment
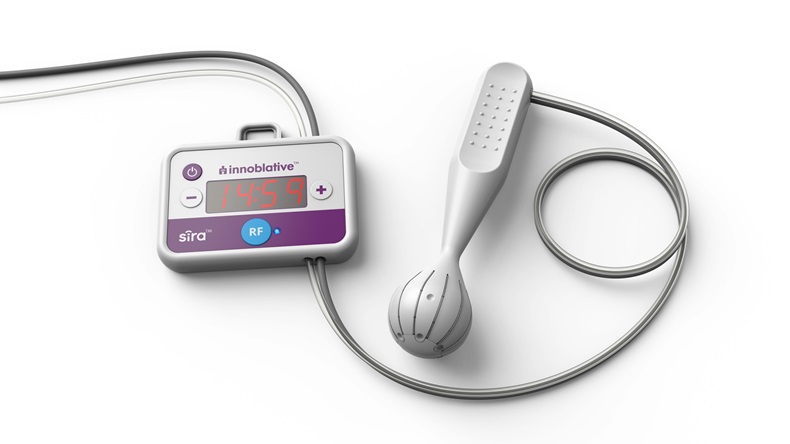
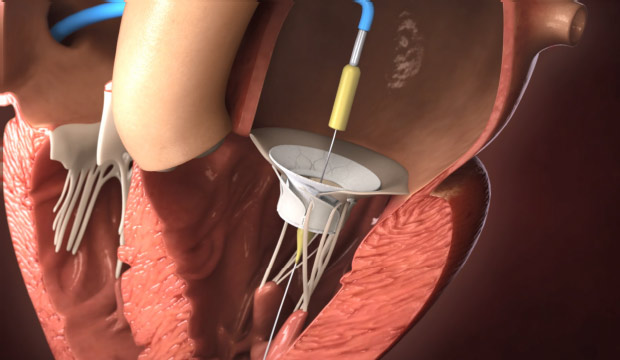
- Novel Electrosurgical Device Could Be a Game-Changer for Breast Cancer Treatment
- New Robotic Navigation Platform Provides Surgeons Best-In-Class Solution for Orthopedic Treatment
- Breakthrough AR Surgical System Brings Precision-Enhanced Visualization into the OR
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
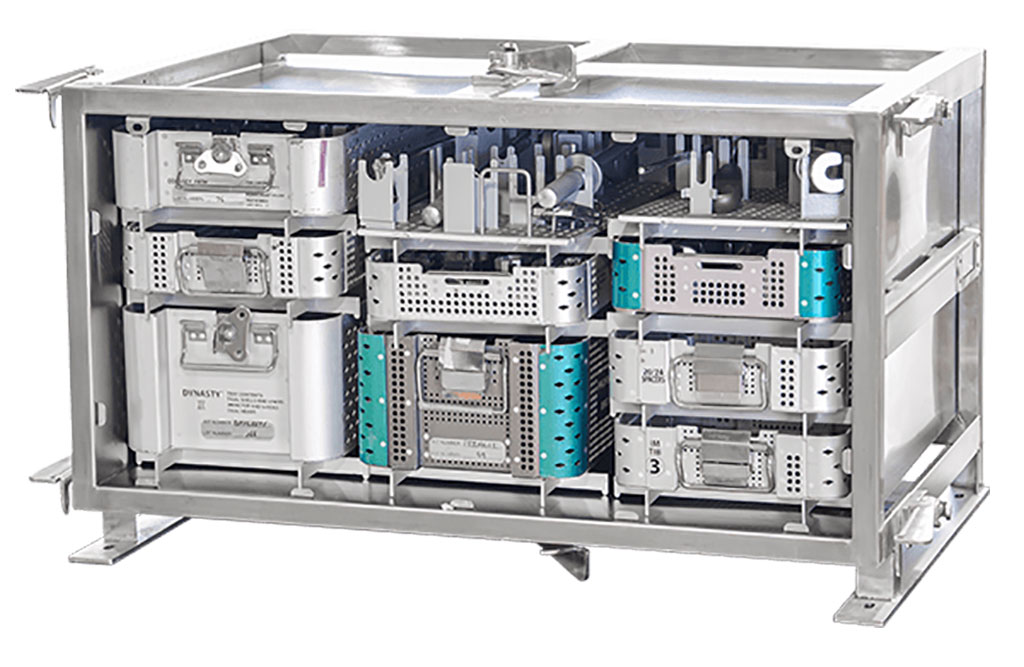
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
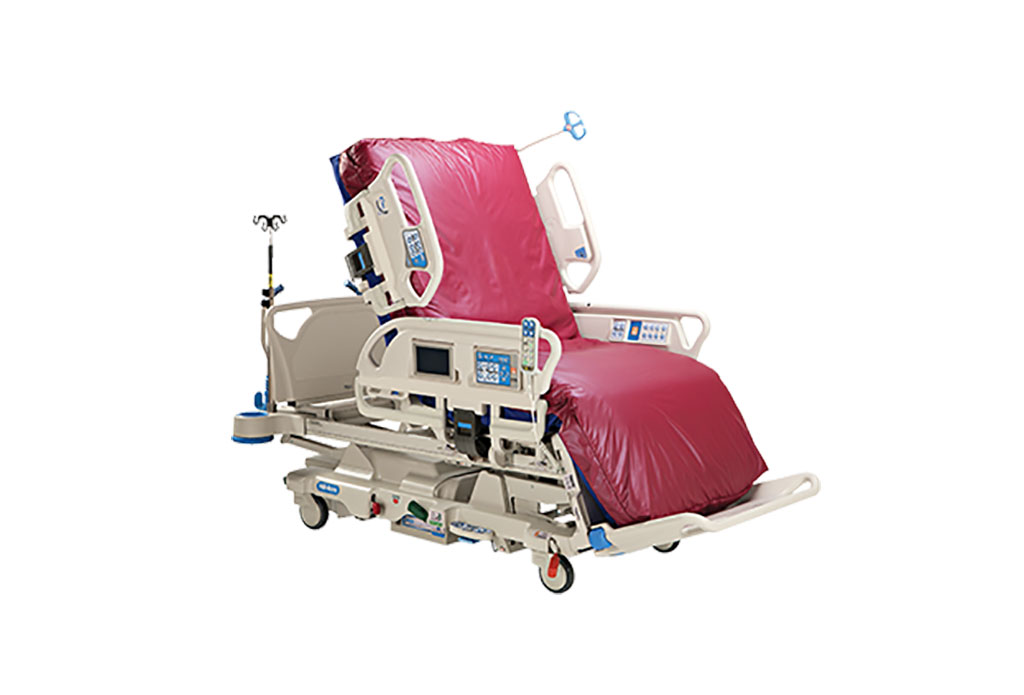
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- International Hospital Federation Awards 2024 Finalists Announced
- 2024 World Medical Tourism Conference and Medical Tourism Expo to Showcase Latest Innovations
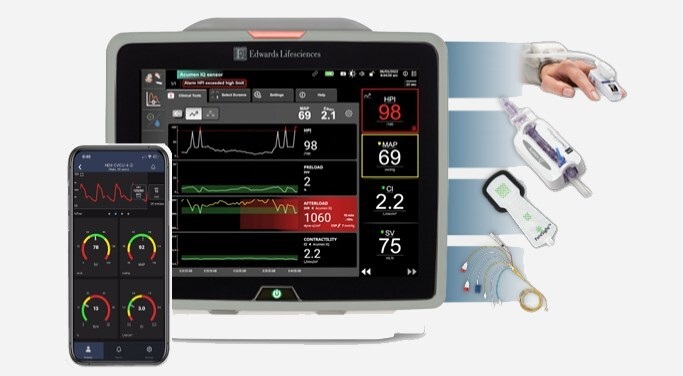
- BD Acquires Edwards Lifesciences' Critical Care Product Group for USD 4.2 Billion
- MEDICA INNOVATION FORUM for the Healthcare Innovations of the Future
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Medical Device Company Shockwave Medical
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
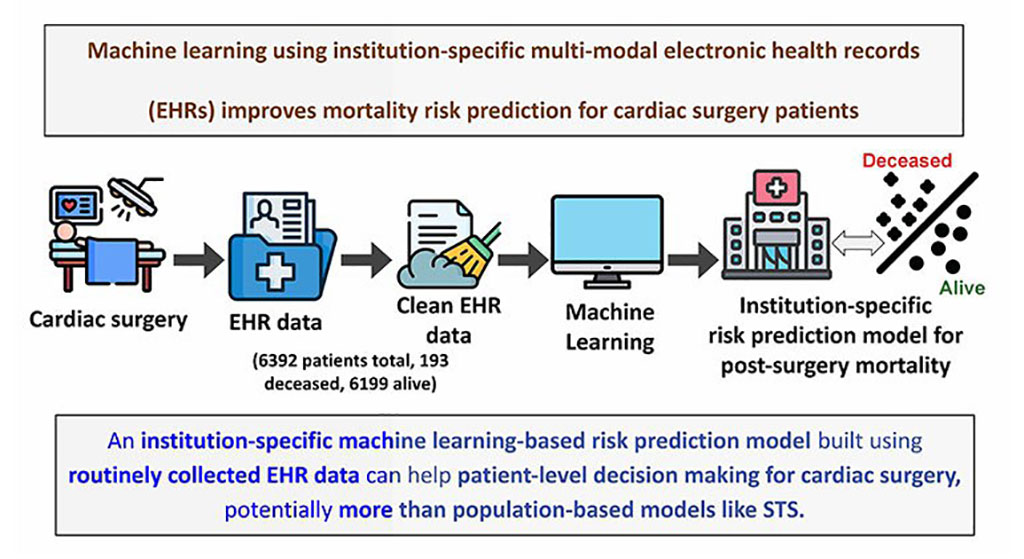
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
Critical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
Critical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Point-Of-Care EEG System Significantly Reduces Length of Patient Stay in ICU
- High-Quality Thin Film Conductor Paves Way for Wearable Electronics with Longer Life Batteries
- Intraoral Camera for Cancer Screening Eliminates Guesswork in Interpreting Clinical Findings
- AI Algorithm Non-Invasively Measures Intracranial Pressure in ICU Patients Following Traumatic Brain Injury
- Healthcare Device Powered By Body Heat Marks First Step Toward Battery-Free Wearable Electronics
- Novel Fluorescent Imaging Agent Helps Surgeons Visualize Missed Lung Tumors
- EHR–Based Nudge Intervention for Surgeons to Reduce Breast Cancer Overtreatment
- Novel Electrosurgical Device Could Be a Game-Changer for Breast Cancer Treatment
- New Robotic Navigation Platform Provides Surgeons Best-In-Class Solution for Orthopedic Treatment
- Breakthrough AR Surgical System Brings Precision-Enhanced Visualization into the OR
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- International Hospital Federation Awards 2024 Finalists Announced
- 2024 World Medical Tourism Conference and Medical Tourism Expo to Showcase Latest Innovations
- BD Acquires Edwards Lifesciences' Critical Care Product Group for USD 4.2 Billion
- MEDICA INNOVATION FORUM for the Healthcare Innovations of the Future
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Medical Device Company Shockwave Medical
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants
- Whole Blood Rapid Test Aids Assessment of Concussion at Patient's Bedside
- New Generation Glucose Hospital Meter System Ensures Accurate, Interference-Free and Safe Use






















.jpg)