Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AI
Surgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

- New Nanomaterial Kills Cancer Cells While Sparring Healthy Tissues
- AI Model Accurately Predicts Neurological Recovery After Cardiac Arrest
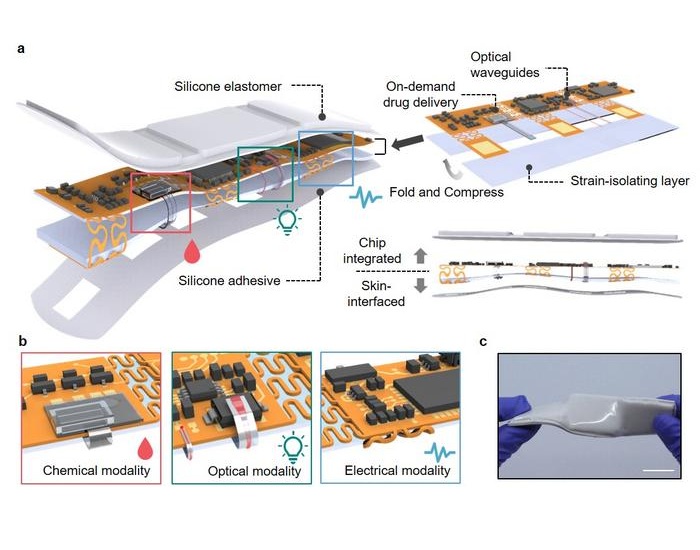
- Battery-Free Nano-Sensors Pave Way for Next-Generation Wearables
- Imaging Technology Detects Early Signs of Cardiovascular Risk Through Skin
- New Therapeutic Approach Marks Breakthrough in Pediatric Heart Disease
- New AI Approach to Improve Surgical Imaging
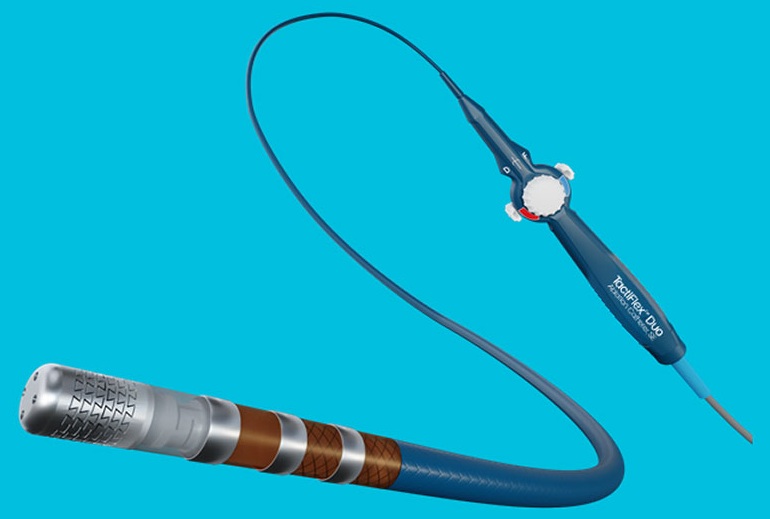
- Dual-Energy Catheter Brings New Flexibility to AFib Ablation
- 3D Bioprinting Pushes Boundaries in Quest for Custom Livers
- First-Of-Its-Kind Probe Monitors Fetal Health in Utero During Surgery
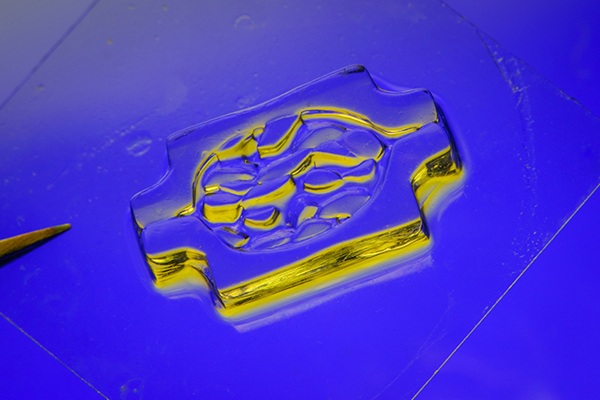
- Light-Activated Tissue Adhesive Patch Achieves Rapid and Watertight Neurosurgical Sealing
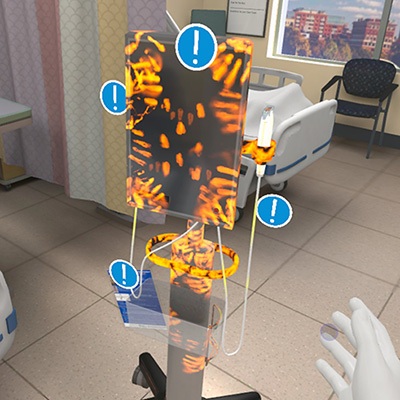
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market
- Philips and Masimo Partner to Advance Patient Monitoring Measurement Technologies
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery

 Expo
Expo
- New Nanomaterial Kills Cancer Cells While Sparring Healthy Tissues
- AI Model Accurately Predicts Neurological Recovery After Cardiac Arrest
- Battery-Free Nano-Sensors Pave Way for Next-Generation Wearables
- Imaging Technology Detects Early Signs of Cardiovascular Risk Through Skin
- New Therapeutic Approach Marks Breakthrough in Pediatric Heart Disease
- New AI Approach to Improve Surgical Imaging
- Dual-Energy Catheter Brings New Flexibility to AFib Ablation
- 3D Bioprinting Pushes Boundaries in Quest for Custom Livers
- First-Of-Its-Kind Probe Monitors Fetal Health in Utero During Surgery
- Light-Activated Tissue Adhesive Patch Achieves Rapid and Watertight Neurosurgical Sealing
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market
- Philips and Masimo Partner to Advance Patient Monitoring Measurement Technologies
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery