Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

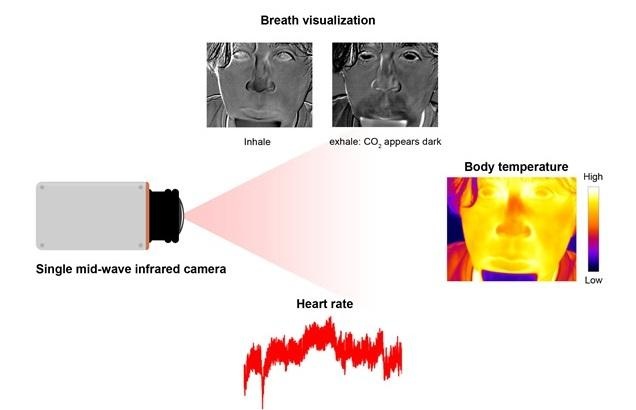
- Single Mid-Wave Infrared Thermal Camera Enables Noncontact Vital Signs Monitoring
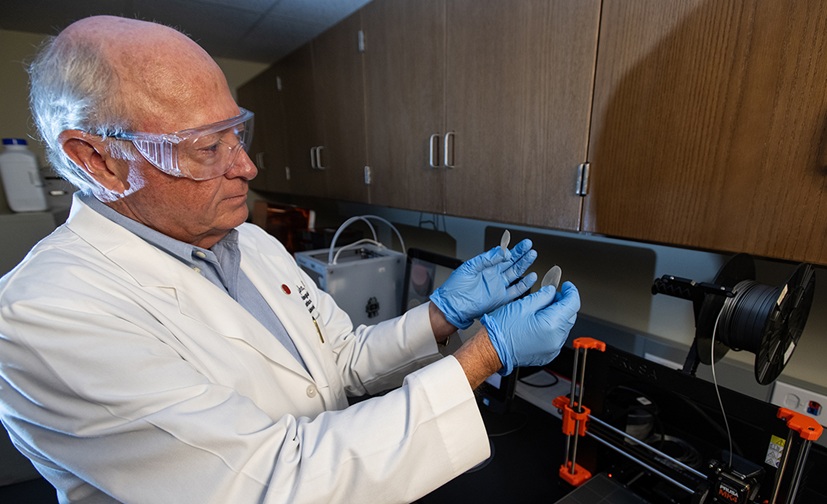
- 3D-Printed Bandage to Help Heal Chronic Wounds
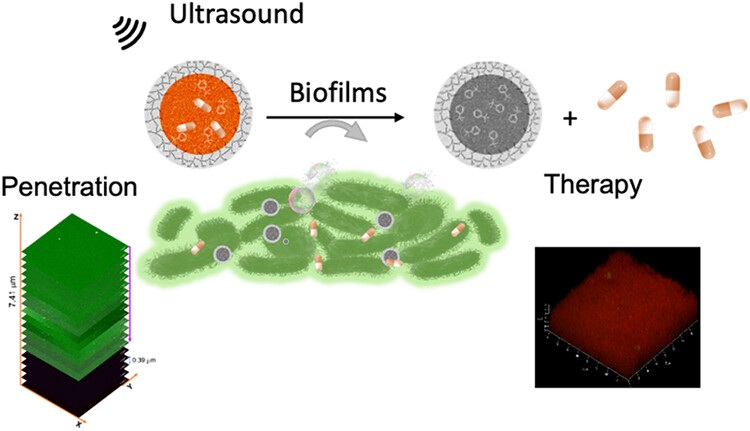
- Ultrasound-Activated Nanoagents Kill Superbugs Hiding in Biofilms
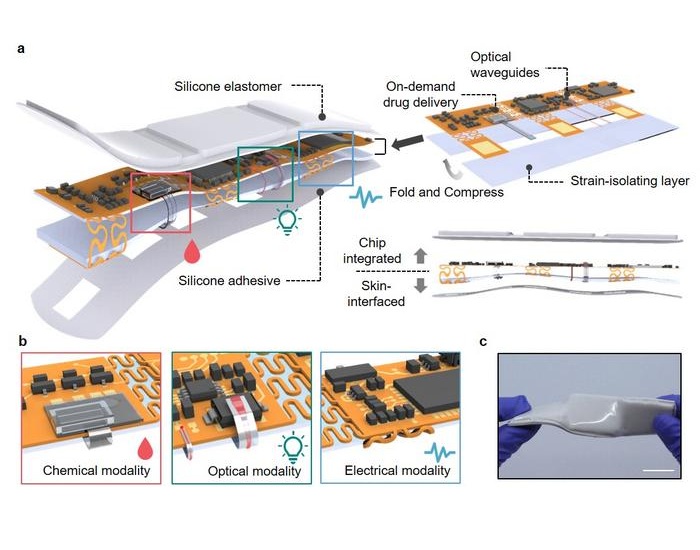
- Painless Microneedle Skin Patch Monitors Immune Health
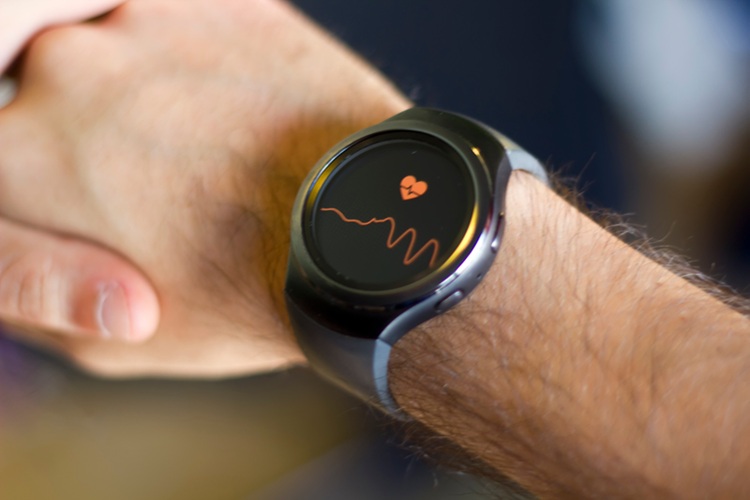
- Smart T-Shirt Uses AI to Enhance Detection of Heart Rhythm Disorders
- Fluorescence Probe Paired with Engineered Enzymes Lights Up Tumors for Easier Surgical Removal
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Effectively Treats Small Kidney Cancers
- Neurostimulation Implant Reduces Seizure Burden in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
- Novel Hydrogel Could Become Bone Implant of the Future
- Skull Implant Design Could Shape Surgical Outcomes
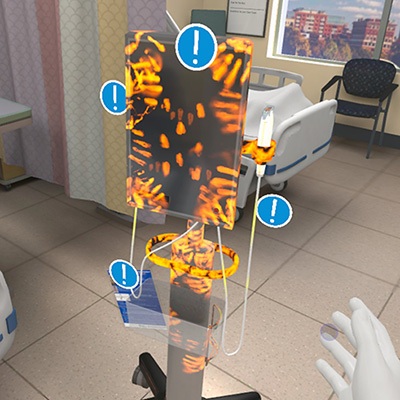
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
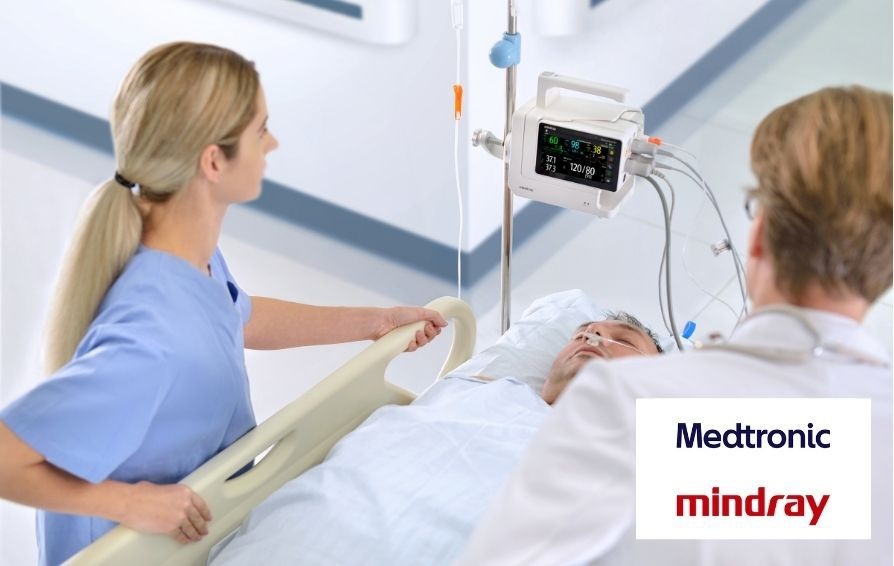
- Medtronic and Mindray Expand Strategic Partnership to Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the U.S.
- FDA Clearance Expands Robotic Options for Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market

 Expo
Expo
- Single Mid-Wave Infrared Thermal Camera Enables Noncontact Vital Signs Monitoring
- 3D-Printed Bandage to Help Heal Chronic Wounds
- Ultrasound-Activated Nanoagents Kill Superbugs Hiding in Biofilms
- Painless Microneedle Skin Patch Monitors Immune Health
- Smart T-Shirt Uses AI to Enhance Detection of Heart Rhythm Disorders
- Fluorescence Probe Paired with Engineered Enzymes Lights Up Tumors for Easier Surgical Removal
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Effectively Treats Small Kidney Cancers
- Neurostimulation Implant Reduces Seizure Burden in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
- Novel Hydrogel Could Become Bone Implant of the Future
- Skull Implant Design Could Shape Surgical Outcomes
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic and Mindray Expand Strategic Partnership to Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the U.S.
- FDA Clearance Expands Robotic Options for Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market