Expo
Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

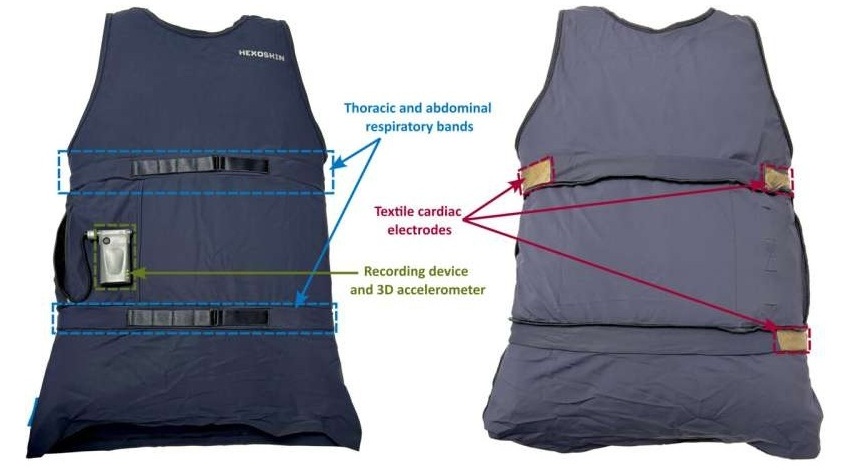
- 'Smart' Shirt Detects Epileptic Seizures in Real Time
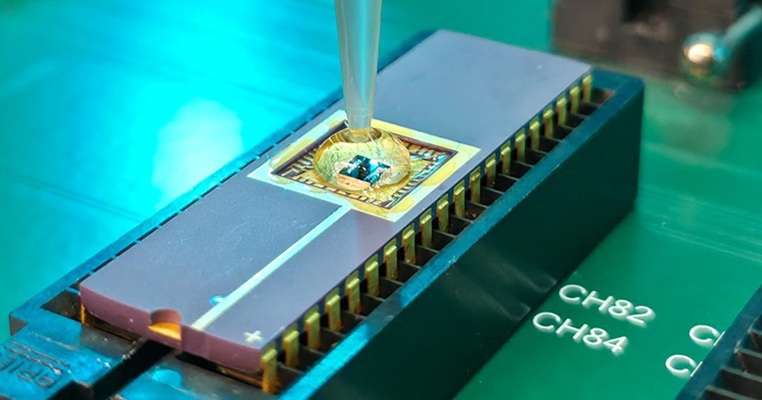
- Skin Patch Measures Effectiveness of Flu/COVID Vaccines in 10 Minutes
- Complete Revascularization Reduces Risk of Death from Cardiovascular Causes
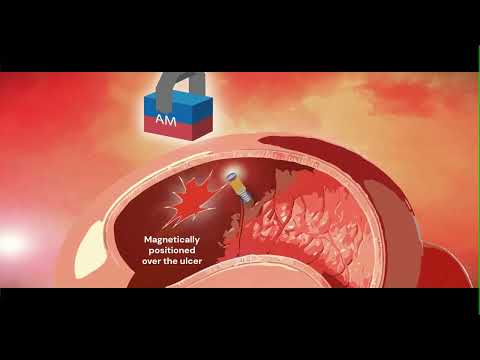
- Tiny Fish-Inspired Robots Navigate Through Body to Deliver Targeted Drug Therapy
- Sweat-Powered Sticker Turns Drinking Cup into Health Sensor
- Optical Tracking Method Identifies Target Areas in Robot-Assisted Neurosurgery
- General Anesthesia Improves Post-Surgery Outcomes for Acute Stroke Patients
- Drug-Coated Balloons Can Replace Stents Even in Larger Coronary Arteries
- Magnetic Kidney Stone Retrieval Device Outperforms Ureteroscopic Laser Lithotripsy
- Absorbable Skull Device Could Replace Traditional Metal Implants Used After Brain Surgery
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Medica
Expo
Medica
- 'Smart' Shirt Detects Epileptic Seizures in Real Time
- Skin Patch Measures Effectiveness of Flu/COVID Vaccines in 10 Minutes
- Complete Revascularization Reduces Risk of Death from Cardiovascular Causes
- Tiny Fish-Inspired Robots Navigate Through Body to Deliver Targeted Drug Therapy
- Sweat-Powered Sticker Turns Drinking Cup into Health Sensor
- Optical Tracking Method Identifies Target Areas in Robot-Assisted Neurosurgery
- General Anesthesia Improves Post-Surgery Outcomes for Acute Stroke Patients
- Drug-Coated Balloons Can Replace Stents Even in Larger Coronary Arteries
- Magnetic Kidney Stone Retrieval Device Outperforms Ureteroscopic Laser Lithotripsy
- Absorbable Skull Device Could Replace Traditional Metal Implants Used After Brain Surgery
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation
- Richard Wolf to Present Innovative System Solutions at Germany Trade Show
- PROTEC to Launch New Motorized PRS 500 B X-ray System
- Randox to Showcase Future-Proofing Diagnostic Technology at Trade Fair
- NDS Announces New OR Networking Solution at Germany Trade Show
- Global Good and Motic Announce AI-Powered Microscope at MEDICA 2017
- Rober Showcases Pioneering ‘Zero Pressure’ Mattresses in Germany
- UK Companies Showcase Life-Saving Solutions at Medica 2018
- Siemens Healthineers Showcases ACUSON Ultrasound Product Portfolio
- Metaltronica Presents Digital Mammography Systems at Medical Trade Fair
- Canon Displays New Products at MEDICA Show
- Samsung Medison Exhibits New HERA I10 Combination Ultrasound System
- Medtronic Displays Patient Monitoring Systems at MEDICA 2019
- Healcerion Exhibits SONON Wireless Handheld Ultrasound at MEDICA 2019
- Hans Rudolph Exhibits Latest Range of Oro-Nasal Masks at MEDICA 2019
- EIZO Demonstrates CuratOR Alipe IP-Based Video Management Solution at MEDICA 2019
- Fisher & Paykel Demonstrates Humidified Nasal High Flow System for Delivering Respiratory Support at MEDICA 2021
- Axcent Medical Showcases Premium ICU Ventilator and Electronic Anesthesia Workstation at MEDICA 2021
- MESI Demonstrates Revolutionary mTABLET System at MEDICA 2021
- Microlife Presents the Only Blood Pressure Monitor with Integrated AFIB Detection at MEDICA 2021
- Innovative Health Presents Its Breakthrough Versatile and Low Cost Non-Electric Infusion System at MEDICA 2021
- Huntleigh Exhibits Range of Vital Signs Monitoring Solutions at MEDICA 2022
- Owen Mumford Presents Cutting-Edge Capillary Blood Sampling Devices for POC Testing
- Noul Demonstrates AI-Driven On-Site Diagnostics Platform at MEDICA 2022
- KUKA Presents Robot-Based Assistance Systems at MEDICA 2022
- Heyer Medical Exhibits State-Of-The-Art Ventilators, Anesthesia Workstations and Surgical Lights
- LG Electronics Exhibits High Resolution Monitors for Surgery and Medical Diagnosis
- Advantech Demonstrates High-Performance Healthcare Systems and Solutions
- MAVIG Highlights X-Ray Protective Clothing and Suspension Systems for Medical Equipment
- EIZO GmbH Presents New 4K Visualization Solutions for Operating Room
- OptoMedic Showcases World of Fluorescence Endoscopy Technologies
- Norav Medical Demonstrates Advanced ECG Solutions
- MAVIG Highlights Latest Innovations in X-Ray Protection and Medical Suspension Systems
- EndoSemio Features Wireless Endoscope Tracheostomy Kit for Advanced Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Brain Navi Demonstrates First Autonomous Surgical Navigation Robot for Neurosurgery
- Winners Announced of the 14th MEDICA Start-up Competition
- Hurotics Demonstrates Advanced Gait Rehabilitation Exosuit at MEDICA 2025
- CETA Testsysteme Brings Advanced Leak and Flow Testing Technologies to MEDICA 2025
- Surgical Holdings Highlights Growth and Collaboration as Part of the Stille Group at MEDICA 2025
- WEGO Medical Brings Advanced Blood Management and Surgical Technologies to MEDICA 2025