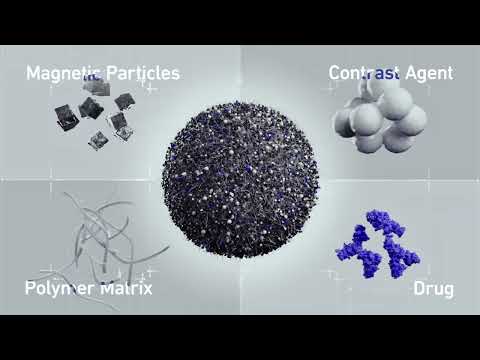
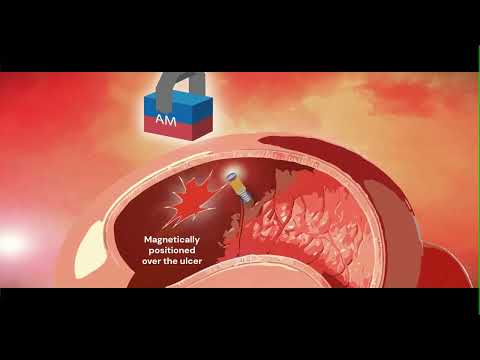
Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical Care
Patient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

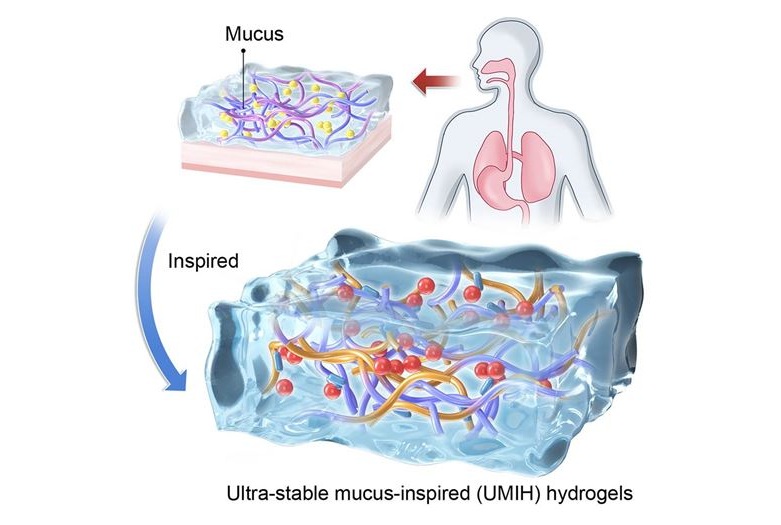
- Ultra-Stable Mucus-Inspired Hydrogel Boosts Gastrointestinal Wound Healing
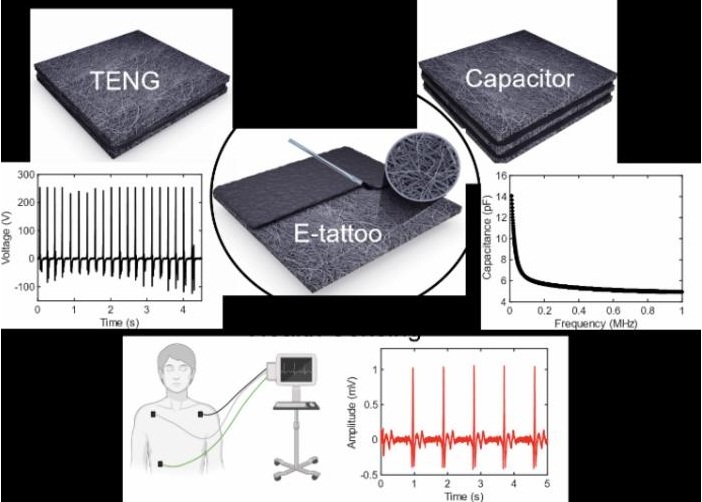
- E-Tattoos Harvest Energy and Monitor Health in Real Time
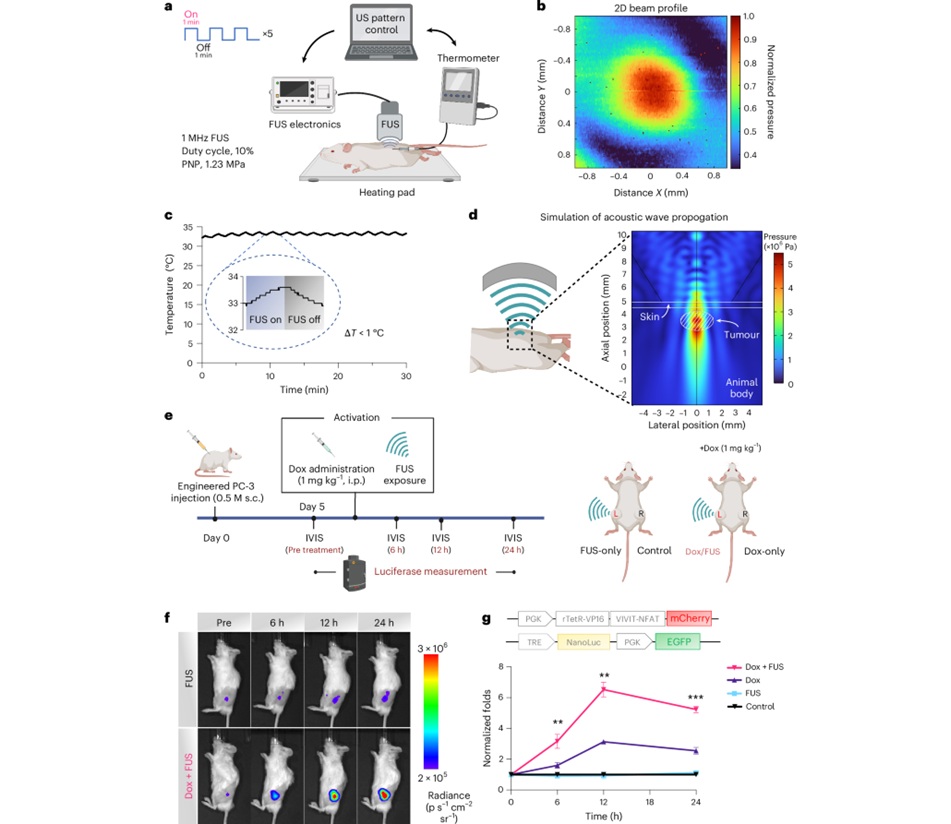
- Focused Ultrasound Tricks Tumors into Marking Themselves for Destruction
- World's Smallest Programmable Robot Opens Up New Possibilities in Medicine
- Remote Ventilate View Platform Enables Real-Time Monitoring of Patient-Ventilator Asynchrony
- NIR Light Enables Powering and Communicating with Implantable Medical Devices
- Simple Bypass Protocol Improves Outcomes in Chronic Cerebral Occlusion
- Implantable Absorbable Sensor Detects Life-Threatening Complications After Intestinal Surgery
- New Study Findings Enable Improved Ventilation During Complex Lung Surgery
- 3D-Printed Blood Vessel Scaffolds Could Transform Heart Bypass Surgeries
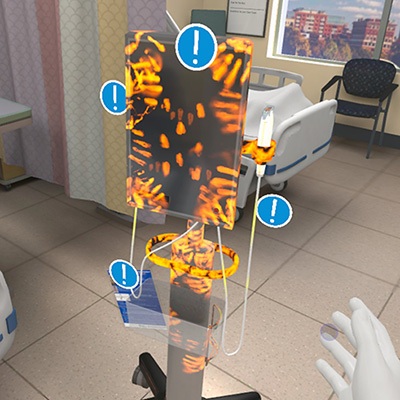
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- Ultra-Stable Mucus-Inspired Hydrogel Boosts Gastrointestinal Wound Healing
- E-Tattoos Harvest Energy and Monitor Health in Real Time
- Focused Ultrasound Tricks Tumors into Marking Themselves for Destruction
- World's Smallest Programmable Robot Opens Up New Possibilities in Medicine
- Remote Ventilate View Platform Enables Real-Time Monitoring of Patient-Ventilator Asynchrony
- NIR Light Enables Powering and Communicating with Implantable Medical Devices
- Simple Bypass Protocol Improves Outcomes in Chronic Cerebral Occlusion
- Implantable Absorbable Sensor Detects Life-Threatening Complications After Intestinal Surgery
- New Study Findings Enable Improved Ventilation During Complex Lung Surgery
- 3D-Printed Blood Vessel Scaffolds Could Transform Heart Bypass Surgeries
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation