Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events

- Next-Gen Wearable Continuous Glucose Monitoring System to Revolutionize Diabetes Management
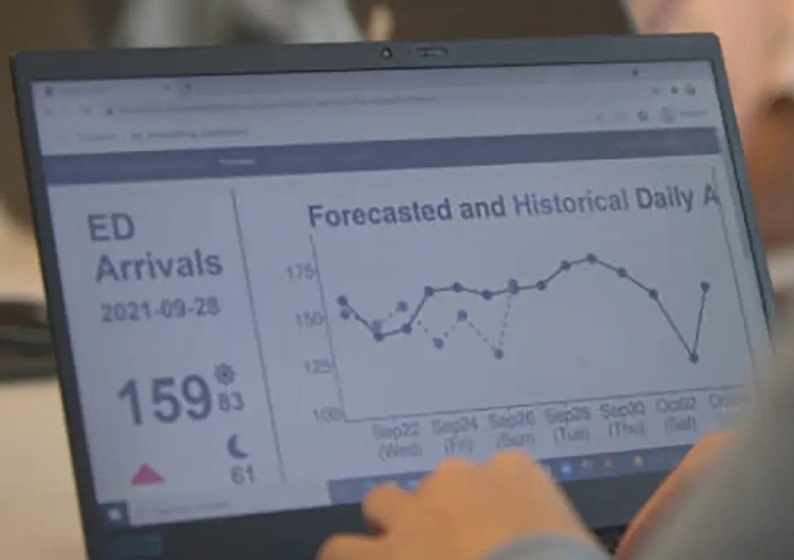
- Machine Learning Could Reduce Hospitalizations by 30% During Pandemic
- AI-Based System Reduces Risk of Unexpected Deaths in Hospitalized Patients
- Pioneering Application Detects Pulse Pressure Using Smartphone
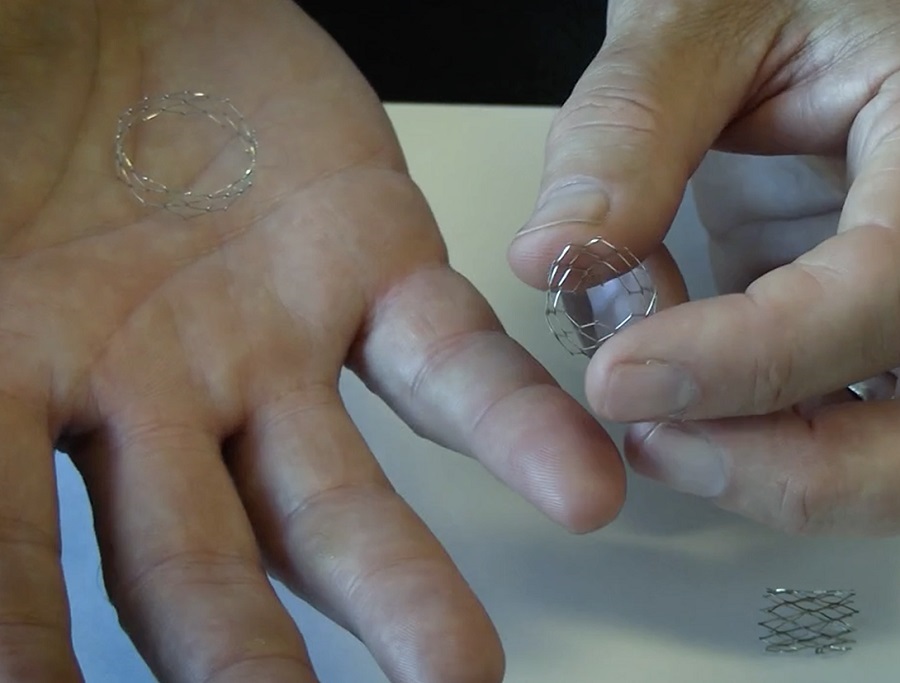
- Mitral Valve Repair Via Catheter Offers Better Outcomes Than Pharmacological Treatment in Heart Failure Patients
- Better-Designed Operating Room Shortens Surgical Procedure Time and Produces Better Outcomes
- Spatial Computing Technology Could Revolutionize Operating Room Environment
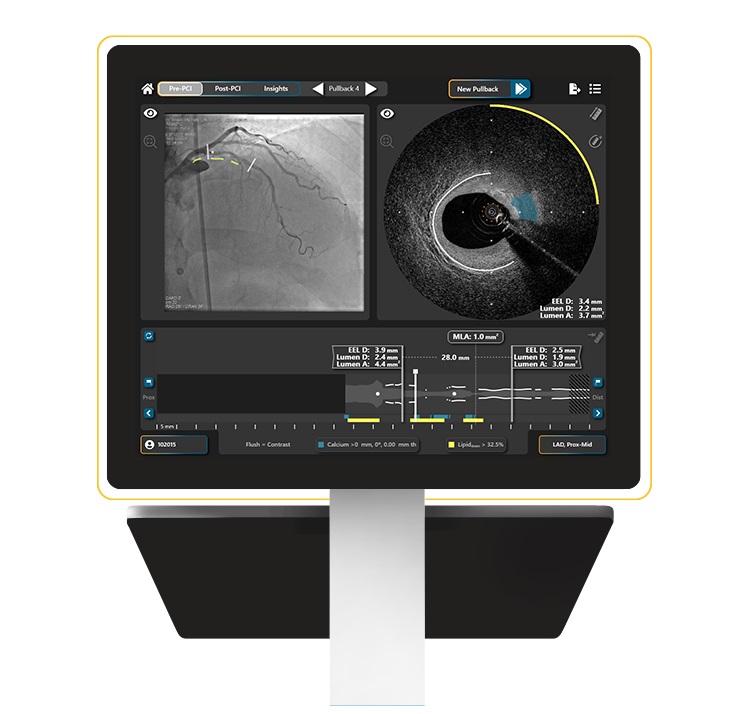
- Innovative Catheter Guidance Technology Aims for Zero Malpositioning
- Breakthrough Heart Valve Combines Best of Mechanical and Tissue Replacement Technology
- Ultraportable Battery Powered Medical Device Revolutionizes Concept of Portable Surgical Care
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Abbott and Medtronic Global Partnership to Integrate Advanced Glucose Sensing Technology with Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
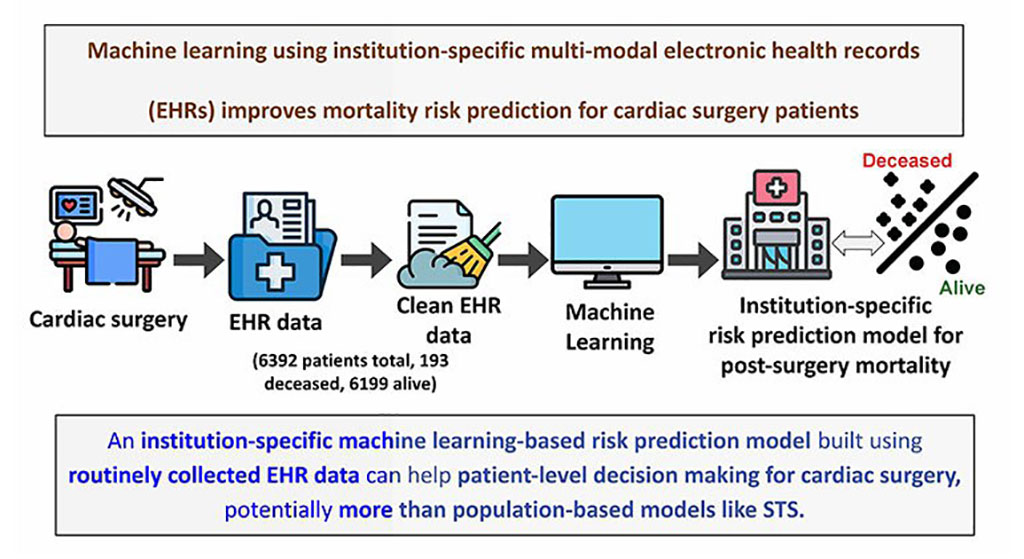
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Advertise with Us


- Next-Gen Wearable Continuous Glucose Monitoring System to Revolutionize Diabetes Management
- Machine Learning Could Reduce Hospitalizations by 30% During Pandemic
- AI-Based System Reduces Risk of Unexpected Deaths in Hospitalized Patients
- Pioneering Application Detects Pulse Pressure Using Smartphone
- Mitral Valve Repair Via Catheter Offers Better Outcomes Than Pharmacological Treatment in Heart Failure Patients
- Better-Designed Operating Room Shortens Surgical Procedure Time and Produces Better Outcomes
- Spatial Computing Technology Could Revolutionize Operating Room Environment
- Innovative Catheter Guidance Technology Aims for Zero Malpositioning
- Breakthrough Heart Valve Combines Best of Mechanical and Tissue Replacement Technology
- Ultraportable Battery Powered Medical Device Revolutionizes Concept of Portable Surgical Care
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Next Gen ICU Bed to Help Address Complex Critical Care Needs
- Groundbreaking AI-Powered UV-C Disinfection Technology Redefines Infection Control Landscape
- Clean Hospitals Can Reduce Antibiotic Resistance, Save Lives
- ZOLL to Acquire Vyaire Medical’s Ventilator Business
- Getinge Acquires Organ Transport Products and Services Company Paragonix Technologies
- Stryker Acquires care.ai to Boost AI-Driven Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson Acquires Cardiovascular Specialist V-Wave
- Abbott and Medtronic Global Partnership to Integrate Advanced Glucose Sensing Technology with Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
- Strategic Collaboration to Develop and Integrate Generative AI into Healthcare
- AI-Enabled Operating Rooms Solution Helps Hospitals Maximize Utilization and Unlock Capacity
- AI Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Three Years before Diagnosis from Patients’ Medical Records
- First Fully Autonomous Generative AI Personalized Medical Authorizations System Reduces Care Delay
- Electronic Health Records May Be Key to Improving Patient Care, Study Finds
- 5-Minute Multiplex PCR Testing System to Redefine Point-Of-Care Diagnostics
- POCT for Infectious Diseases Delivers Laboratory Equivalent Pathology Results
- Cartridge-Based Hemostasis Analyzer System Enables Faster Coagulation Testing
- Critical Bleeding Management System to Help Hospitals Further Standardize Viscoelastic Testing
- Point of Care HIV Test Enables Early Infection Diagnosis for Infants