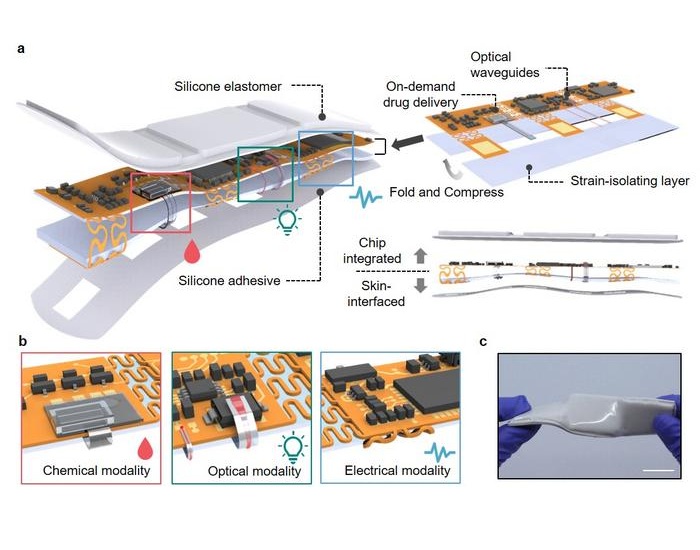
Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

- Wireless Sensing Technology Enables Touch-Free Diagnostics of Common Lung Diseases
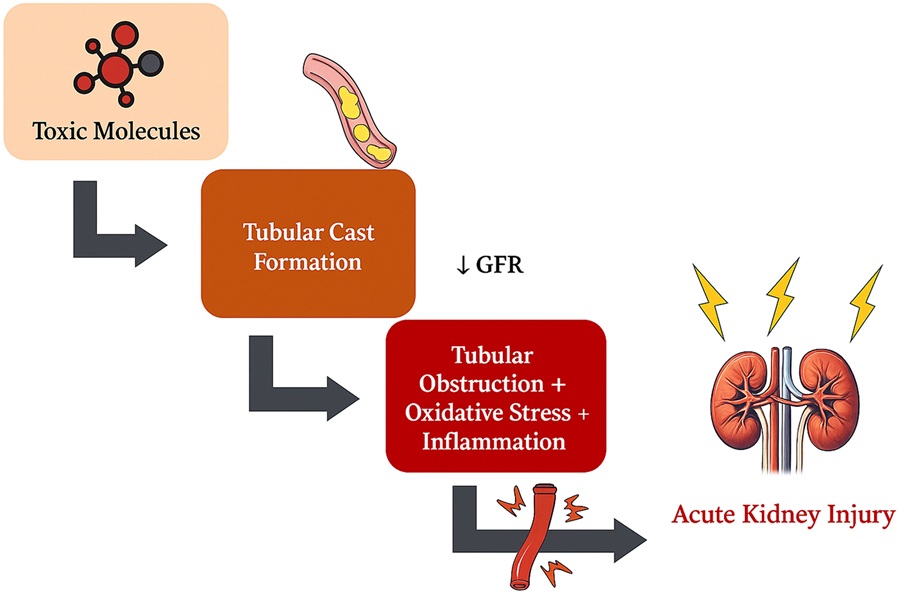
- Early Detection and Targeted Blood Purification Could Prevent Kidney Failure in ICU Patients
- New Cancer Treatment Uses Sound-Responsive Particles to Soften Tumors
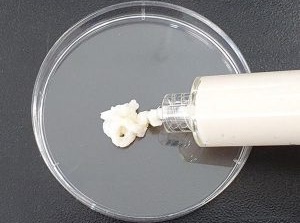
- Sprayable Powder-Type Hemostatic Agent Stops Bleeding in One Second
- AI Model Helps Diagnose Often Undetected Heart Disease from Simple EKG
- Injectable Breast ‘Implant’ Offers Alternative to Traditional Surgeries
- AI Detects Stomach Cancer Risk from Upper Endoscopic Images
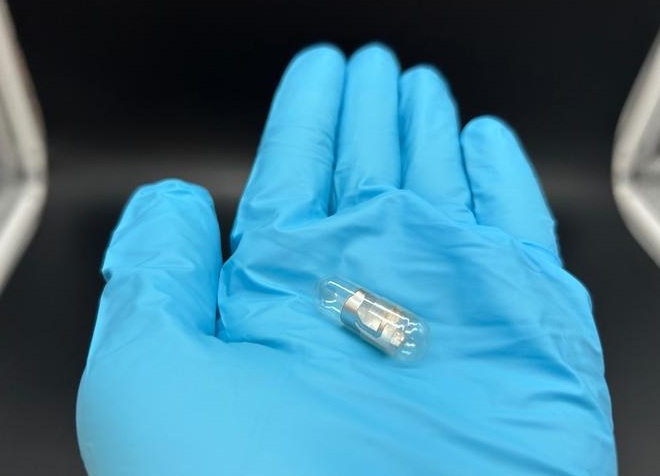
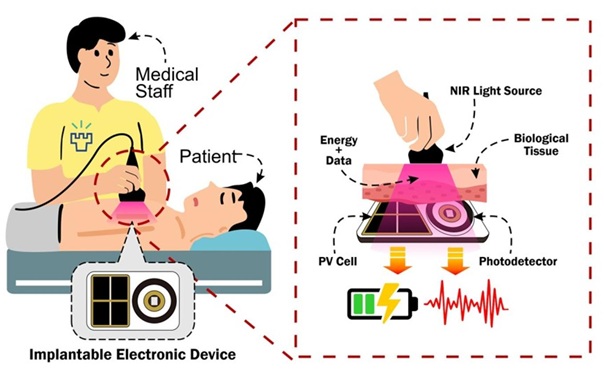
- NIR Light Enables Powering and Communicating with Implantable Medical Devices
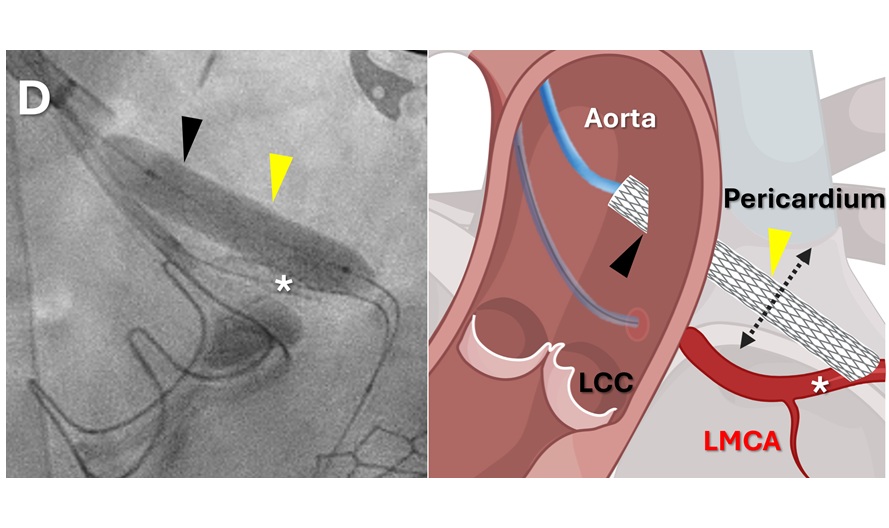
- Simple Bypass Protocol Improves Outcomes in Chronic Cerebral Occlusion
- Implantable Absorbable Sensor Detects Life-Threatening Complications After Intestinal Surgery
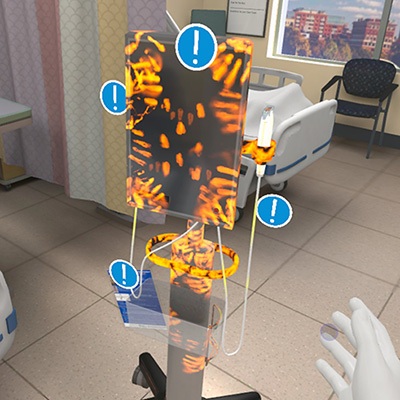
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- Wireless Sensing Technology Enables Touch-Free Diagnostics of Common Lung Diseases
- Early Detection and Targeted Blood Purification Could Prevent Kidney Failure in ICU Patients
- New Cancer Treatment Uses Sound-Responsive Particles to Soften Tumors
- Sprayable Powder-Type Hemostatic Agent Stops Bleeding in One Second
- AI Model Helps Diagnose Often Undetected Heart Disease from Simple EKG
- Injectable Breast ‘Implant’ Offers Alternative to Traditional Surgeries
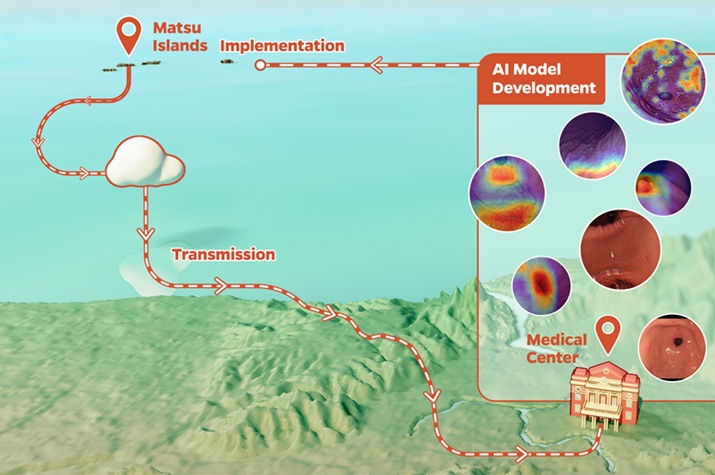
- AI Detects Stomach Cancer Risk from Upper Endoscopic Images
- NIR Light Enables Powering and Communicating with Implantable Medical Devices
- Simple Bypass Protocol Improves Outcomes in Chronic Cerebral Occlusion
- Implantable Absorbable Sensor Detects Life-Threatening Complications After Intestinal Surgery
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation






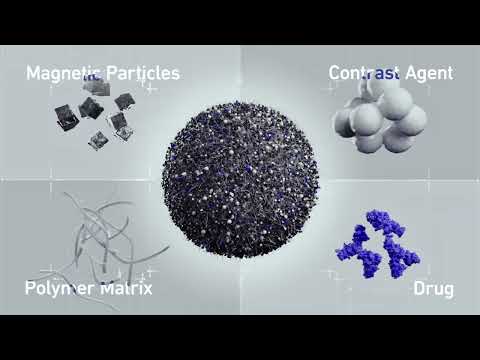

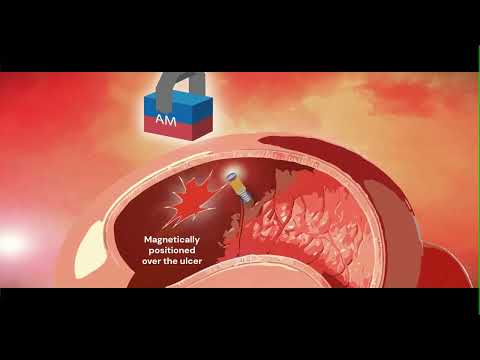






.jpg)