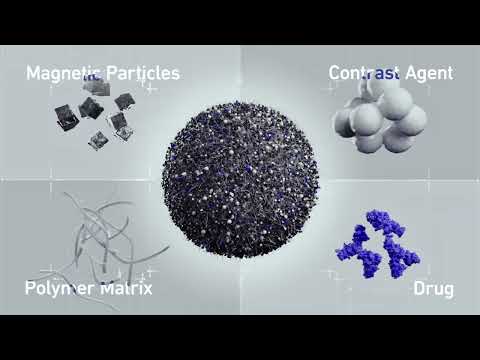
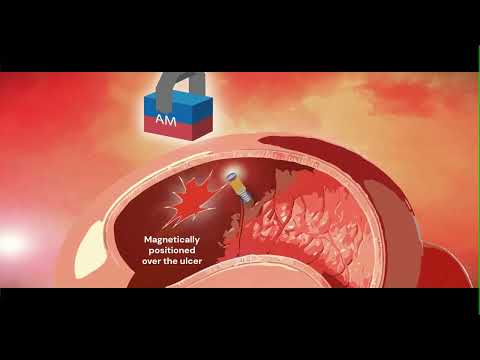
Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical TechniquesPatient CareHealth ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

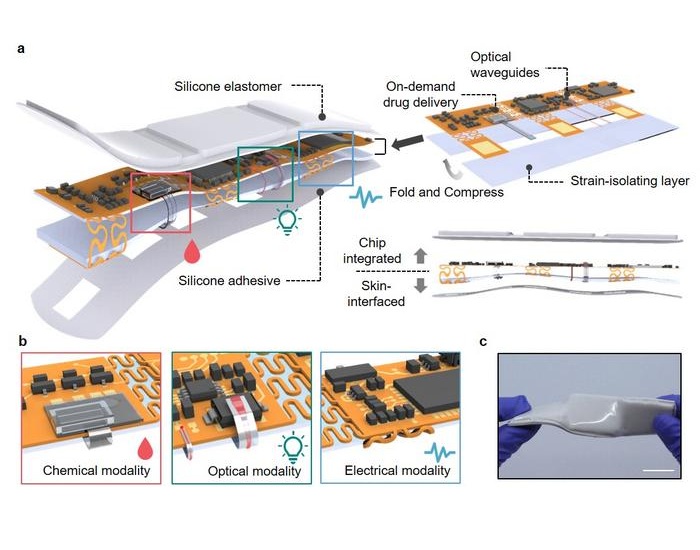
- Breathable Electronic Skin Paves Way for Next-Generation Wearable Devices
- AI Transforming Colon Cancer Diagnosis
- Ventricular Assist Device Offers Long-Term Use in Children Waiting for Donor Heart
- Precision Approach Improves Immunotherapy Effectiveness for ICU Patients with Sepsis
- Soft Robots Could Donate Their Heart to Humans
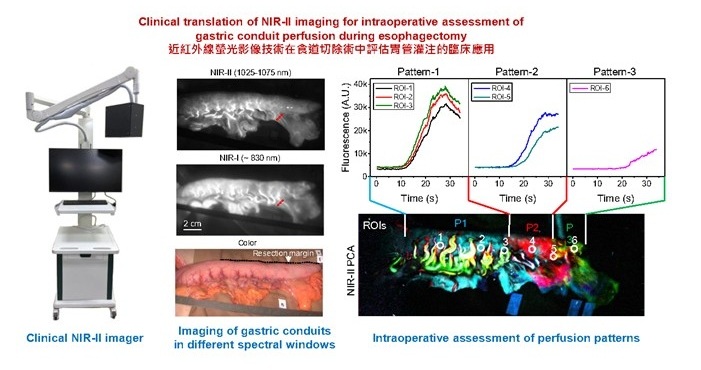
- Novel Imaging Technique Helps View Blood Perfusion During Esophageal Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Surgery Proven Safe and Effective for Complex ‘Whipple’ Procedure
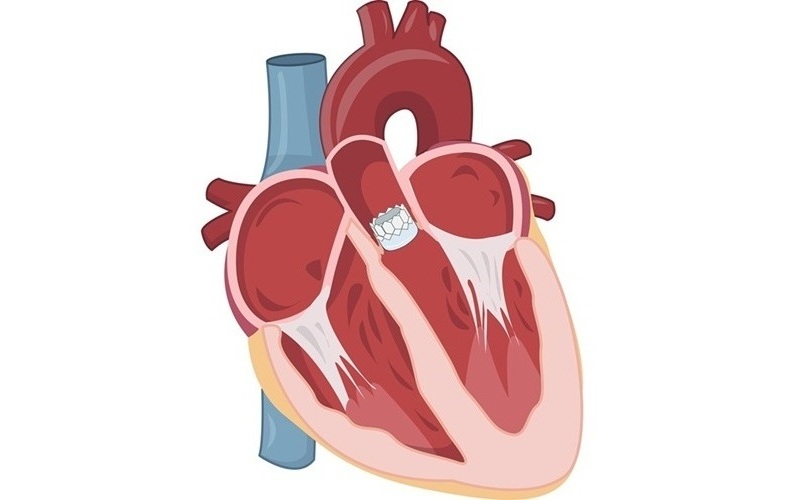
- Catheter-Based Procedures Offer Less Invasive Option for Treatment of Valvular Disease
- Laparoscopic Surgery Improves Outcomes for Severe Newborn Liver Disease
- Novel Endoscopy Technique Provides Access to Deep Lung Tumors
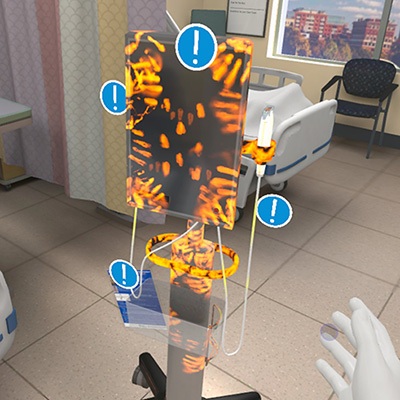
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation

 Expo
Expo
- Breathable Electronic Skin Paves Way for Next-Generation Wearable Devices
- AI Transforming Colon Cancer Diagnosis
- Ventricular Assist Device Offers Long-Term Use in Children Waiting for Donor Heart
- Precision Approach Improves Immunotherapy Effectiveness for ICU Patients with Sepsis
- Soft Robots Could Donate Their Heart to Humans
- Novel Imaging Technique Helps View Blood Perfusion During Esophageal Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Surgery Proven Safe and Effective for Complex ‘Whipple’ Procedure
- Catheter-Based Procedures Offer Less Invasive Option for Treatment of Valvular Disease
- Laparoscopic Surgery Improves Outcomes for Severe Newborn Liver Disease
- Novel Endoscopy Technique Provides Access to Deep Lung Tumors
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- B. Braun Acquires Digital Microsurgery Company True Digital Surgery
- CMEF 2025 to Promote Holistic and High-Quality Development of Medical and Health Industry
- Bayer and Broad Institute Extend Research Collaboration to Develop New Cardiovascular Therapies
- Medtronic Partners with Corsano to Expand Acute Care & Monitoring Portfolio in Europe
- Expanded Collaboration to Transform OR Technology Through AI and Automation