Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Medical Imaging
AICritical CareSurgical Techniques
Health ITPoint of CareBusiness
Events
Webinars

- Wearable Device for Diabetics Could Replace Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
- AI Stethoscope Spots Heart Valve Disease Earlier Than GPs
- Bioadhesive Patch Eliminates Cancer Cells That Remain After Brain Tumor Surgery
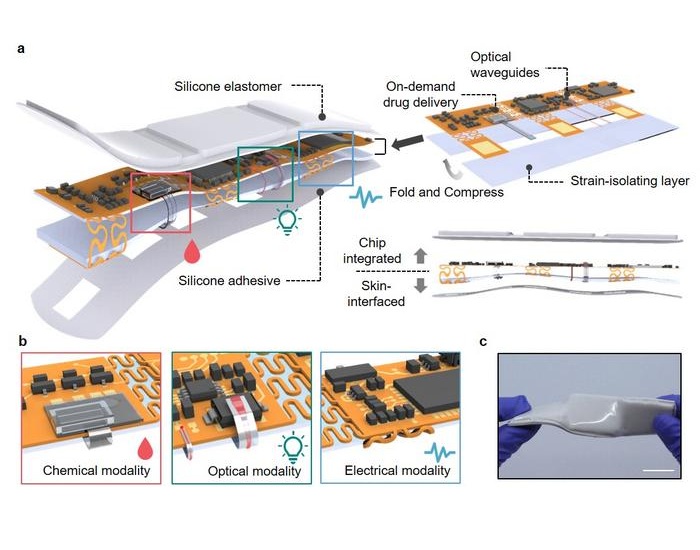
- Wearable Patch Provides Up-To-The-Minute Readouts of Medication Levels in Body
- Living Implant Could End Daily Insulin Injections
- Neural Device Regrows Surrounding Skull After Brain Implantation
- Surgical Innovation Cuts Ovarian Cancer Risk by 80%
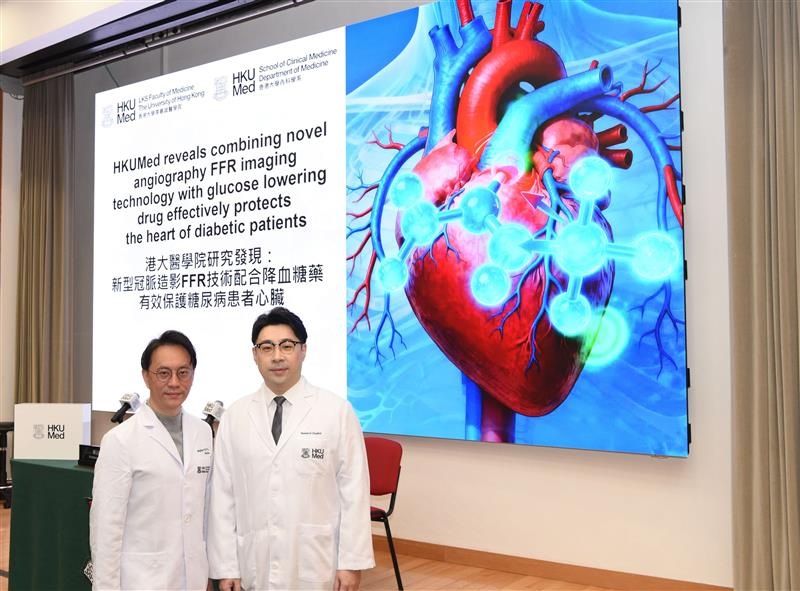
- New Imaging Combo Offers Hope for High-Risk Heart Patients
- New Classification System Brings Clarity to Brain Tumor Surgery Decisions
- Boengineered Tissue Offers New Hope for Secondary Lymphedema Treatment
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
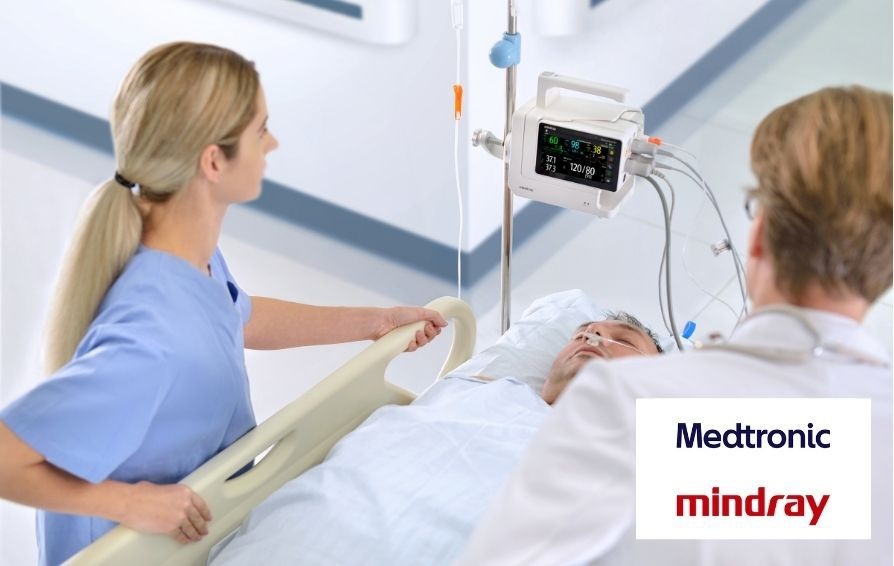
- Medtronic and Mindray Expand Strategic Partnership to Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the U.S.
- FDA Clearance Expands Robotic Options for Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market

 Expo
Expo
- Wearable Device for Diabetics Could Replace Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
- AI Stethoscope Spots Heart Valve Disease Earlier Than GPs
- Bioadhesive Patch Eliminates Cancer Cells That Remain After Brain Tumor Surgery
- Wearable Patch Provides Up-To-The-Minute Readouts of Medication Levels in Body
- Living Implant Could End Daily Insulin Injections
- Neural Device Regrows Surrounding Skull After Brain Implantation
- Surgical Innovation Cuts Ovarian Cancer Risk by 80%
- New Imaging Combo Offers Hope for High-Risk Heart Patients
- New Classification System Brings Clarity to Brain Tumor Surgery Decisions
- Boengineered Tissue Offers New Hope for Secondary Lymphedema Treatment
- VR Training Tool Combats Contamination of Portable Medical Equipment
- Portable Biosensor Platform to Reduce Hospital-Acquired Infections
- First-Of-Its-Kind Portable Germicidal Light Technology Disinfects High-Touch Clinical Surfaces in Seconds
- Surgical Capacity Optimization Solution Helps Hospitals Boost OR Utilization
- Game-Changing Innovation in Surgical Instrument Sterilization Significantly Improves OR Throughput
- Medtronic and Mindray Expand Strategic Partnership to Ambulatory Surgery Centers in the U.S.
- FDA Clearance Expands Robotic Options for Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to debut specialised Biotech & Life Sciences Zone as sector growth accelerates globally
- WHX in Dubai (formerly Arab Health) to bring together key UAE government entities during the groundbreaking 2026 edition
- Interoperability Push Fuels Surge in Healthcare IT Market